Bitumen is a beneficial material that is used in various industries. More than 85% of the world’s bitumen production is used for road construction, 10% is used in other constructions and 5% is used in a variety of other industries, including insulation.
Read the rest of this article to know more about bitumen.
What is Bitumen? Bitumen Meaning & Definition
Bitumen is a viscous substance that exists in a liquid to a semi-solid phase. It has a blackish-brown color.
It is generally composed of asphaltene resin and other petroleum compounds.
Different compositions of bitumen result in different properties.
You can read the bitumen production process page to know more details about bitumen manufacturing.
Origin of Bitumen
Bitumen is found in nature and also can be extracted from crude oil.
1- Bitumen of Natural Origin
Million years ago, living organisms such as microscopic algae (diatoms) were buried under sedimentary rocks, in swamps, and in other aquatic habitats.
These residues were converted to natural bitumen under the pressure of the upper sedimentary layers and temperatures above 50 °C.
Bitumen is now found in hills and oil lakes. Most of the bitumen resources are in Canada, Venezuela, and Oman. There are also natural bitumen mines in the west of Iran. It has different ash content.
Natural bitumen or Gilsonite has many impurities including sulfur and heavy metals. The cost of extracting and using this bitumen is higher than the bitumen obtained from crude oil.
It is usually used as an additive for waterproofing coating, mud drilling, and road construction.
2. Crude Oil Distillation
Crude oil is the primary source of bitumen for the industry. Crude oil is a mixture of different compounds that is separated by a distillation tower. The remnants of the distillation tower, called vacuum bottom, are transferred to be processed and turned into bitumen.
Different types of bitumen, including penetration bitumen or oxidized bitumen, are produced by a different process on vacuum bottom in the refinery. The main application of this bitumen is in road construction.
Read the different types of bitumen used in road construction to know more details.
To become familiar with the way bitumen is created in nature, how it is extracted from oil, what its classifications are, and what uses it has, watch the below video:
What is the Difference Between Bitumen, Tar, and Asphalt?
In the United States, the words bitumen and asphalt are synonymous, but in general, asphalt means the composition of aggregates and bitumen, as a binder, that is used for road construction.
Bitumen is a hydrocarbon substance. It is found naturally or comes through refining processes from crude oil.
Tar is also a dark hydrocarbon material. But the difference between tar and bitumen is in the origin of their production. The tar is obtained through a special distillation process from wood or coal. Coal-based tar is high in benzene, which is cancer-causing.
Tar is mostly used in road construction. The tar wood has been used for thousands of years in northern Europe to waterproof boats, among other uses. Coal fiber and wood also have medicinal properties and are used to treat psoriasis and eradicate germs.
Read our article about “The difference between bitumen, tar, and asphalt”.


Types of Bitumen and Their Applications
Since various kinds of crude oils give various types of bitumen with completely different properties, grading bitumen is vital.
For grading bitumen based on its properties, refineries use a number of standard tests to measure the viscosity level, penetration value, performance, and consistency of bitumen.
The result of these tests is bitumen penetration grades and viscosity grades.
Other grades of bitumen, including cutback bitumen, oxidized bitumen, and bitumen emulsions are classified based on their production process.
1- Gilsonite (Natural Bitumen)
Gilsonite is natural bitumen with a shiny and smooth and solid appearance. Types of Gilsonite are classified based on their ash contents and the solubility in organic solvents.
Since it is a hard and brittle material, it is mostly used in powder form. Gilsonite composition is close to refinery bitumen.
Sometimes in the road construction industry, the combination of gilsonite with refined bitumen is used. Although it has a higher resistance to water penetration its degree of penetration and deformation is low.
Applications of Gilsonite
- Printing industries
- Painting industry
- Drilling mud and cement
- Asphalt and road construction
- Casting sand additive
- Chemical products
- Improving the quality of bitumen


2- Penetration Grade Bitumen
Penetration bitumen is the most widely used bitumen for road construction.
After production in the refinery, it is classified by bitumen penetration test using a penetrometer apparatus. The deeper the needle penetrates into the bitumen surface, the softer it will be and suitable for colder weather. The most widely used bitumen for road construction is penetration bitumen of 60/70 grade and then grade of 80/100. Furthermore, 60/70 grade is widely used as a waterproofing material in buildings.
To use this bitumen, you should pay attention to the average temperature of the area and the amount of traffic.
In the table below, you can see the different grades of this penetrating bitumen along with its application.
| Different Grades of Bitumen Penetration Grade | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration Grade | Penetration Value | Softening Point | Application |
| 40-50 | 40-50 | 52-60 ° C | Tropical areas Mean T > 24° C |
| 60-70 | 60-70 | 49-56 ° C | Mild climate region 7° C < Mean T < 24° C |
| 85-100 | 85-100 | 45-52 ° C | Cold climate Mean T < 7° C |
| 100-120 | 100-120 | 42-49 ° C | Used for road repairs in cold regions |
3- Viscosity Grade Bitumen
Viscosity grade bitumen is classified based on its viscosity after production of the bitumen in the refinery. This classification is almost newer than penetration classification. The highest consumption of this bitumen is in India.
Viscosity bitumen has four different grades that are VG 10, VG20, VG30, and VG 40. They have different applications.
| Different Grades of Viscosity Grade Bitumen | ||
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity Grade | Viscosity Range at 60°C (Absolute Viscosity) | Typical Applications ∞ |
| VG-10 Bitumen | 800-1200 | Recommended for road construction in cold regions Ideal for spraying Used in production of bitumen emulsion |
| VG-20 Bitumen | 1600-2400 | Used in cold regions for road construction |
| VG-30 Bitumen | 2400-3600 | Maximizes asphalt performance in hot regions A more reliable choice than bitumen pen 60/70 |
| VG-40 Bitumen | 3200-4000 | Works in areas with high traffic loads Well suited for road construction in hot weather |
The reason for using viscosity grading instead of penetration is the change in viscosity of bitumen at high temperatures.
Here are some advantages of VG bitumen to Pen grades:
- This grading system is designed to increase the accuracy of bitumen in hot temperatures. A specific grade of pen bitumen may show various results at a specific temperature, but VG bitumen behaves always the same.
- When there is a need to predict bitumen behavior in the hottest time of the year as well as its properties in normal weather conditions, VG bitumen is a better choice. Since viscosity testing is based on experimenting with bitumen’s properties at three different temperatures (25° C, 60° C, and 135° C), all grades of VG bitumen come with an easier application.


4- Emulsion Bitumen
Bitumen emulsion gets its name from how it is produced. This type of bitumen is a chemical combination of bitumen and water.
It came to the industry to avoid the environmental damages of cutback bitumen. Since water is a reliable alternative to organic solvents to dilute bitumen sufficiently for special applications.
Emulsion bitumen is beneficial to waterproofing, spraying, and tack coats between layers of asphalt pavement.
Read more about the composition of bitumen emulsion in our article “Bitumen emulsion definition, types, and grades”.
Also, you can read about this bitumen grades in the Different Types and Grades of Bitumen Emulsion.
Transporting, handling, and storing bitumen emulsion are all easy, economical, and safe.
Bitumen emulsions are classified based on two main factors:
- Particles’ electrostatic charge
- Breaking or setting time
According to their electronic charge, bitumen emulsions can be anionic (with a negative charge) and cationic (with a positive charge).
The second grading system is based on the time that is needed for a bitumen emulsion to lose water and become sticky enough to bind aggregates.
Various grades of bitumen emulsions have different properties, therefore, each type is suitable for a particular type of application.
Three factors, viscosity level, setting time, and electronic charge of bitumen particles, have an influence on where we use each grade and type of bitumen emulsions.
Bitumen emulsions are less viscous than other grades of bitumen because they are mixed with water and emulsifiers. As a result, we use this type of bitumen for spraying applications.
Bitumen emulsions are also ideal for pavement maintenance and renovating old roads.
Major applications of bitumen emulsions in today’s bitumen industry are tack coats, chip seals, slurry seals, and micro surfacing.


5- Cutback Bitumen
This bitumen is used in industries that require low viscosity bitumen. Cutbacks are also used in cases where bitumen can not be preheated to make asphalt.
To prepare cutback bitumen, penetration bitumen is mixed with organic solvents in a certain amount. These organic solvents include gasoline, naphtha, diesel oil, and furnace oil.
This type of bitumen is suitable for cold climates. The solvents evaporate when bitumen is used.
The cutback is suitable for primer sealing and sprayed sealing.
The only concern was the harm that cutback bitumen had, to the environment. The volatile solvents were hazardous to nature, humans, and the environment.
6- Oxidized Bitumen
Oxidized bitumen is obtained in the refinery by blowing hot air into the penetration bitumen. The oxidized bitumen obtained from this process is chemically stable and has high durability. It is also impermeable to water and is suitable for insulation.
Oxidized bitumen has a lower degree of penetration and higher softening point compared to pure bitumen. Also, it is classified based on these two properties.
Applications of oxidized bitumen include waterproofing in dam construction projects, buildings etc. Also, it is applicable in road construction in combination with other types of bitumen. In other industries, especially oil and gas, it is used to cover pipelines to prevent corrosion.


7- Performance Grade Bitumen (PG Bitumen)
Bitumen Performance Grade is a type of bitumen grading system according to its performance at different temperatures.
A bitumen that can endure at a wide range of temperatures is more suitable.
Classification of PG bitumen is done at high and low temperatures.
The major issue for high-temperature performance is rutting, which normally takes a while to amass. It takes some time for rutting to disappear.
At low temperatures the probability of cracking increases.
To evaluate bitumen’s performance, the average maximum and minimum environment temperatures at which asphalt will be made are chosen.
The bitumen is then exposed to these two temperatures for a week.
The average high and low temperature is increased by 6 °C.
The high temperature in these grades is in the range of 46 to 82 °C and the low temperature in the range is -46 to -10 °C.
Grading bitumen is based on a positive number and a negative number, which indicates the maximum and minimum temperature.
For instance, bitumen PG 64-10 meets the performance factor at an average seven-day maximum pavement temperature of 64 °C and also at a minimum pavement temperature of -10 °C.
If the sum of high and low temperature numbers is more than 90, it will be polymer modified bitumen, and if it is less than 90, it will be unmodified polymer bitumen.
As an example, a PG 76-22 is considered as a polymer-modified binder since the sum is 98. Another example, a PG 64-10 is an unmodified binder.
Thermal cracking is less likely to occur in PG grades 58-34, 64-22, 64-28, and 76-22. In addition, the PG 70-22, 70-28, 76-28, and 82-22 grades are more resistant to rutting.
Note: Due to the black color of asphalt and more heat absorption, the asphalt temperature can be 20 °C higher than the ambient temperature.
Performance grade bitumen is commonly used in construction and reconstruction pavement, sealing edges, sealing cracks in both dense and open grade Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA).
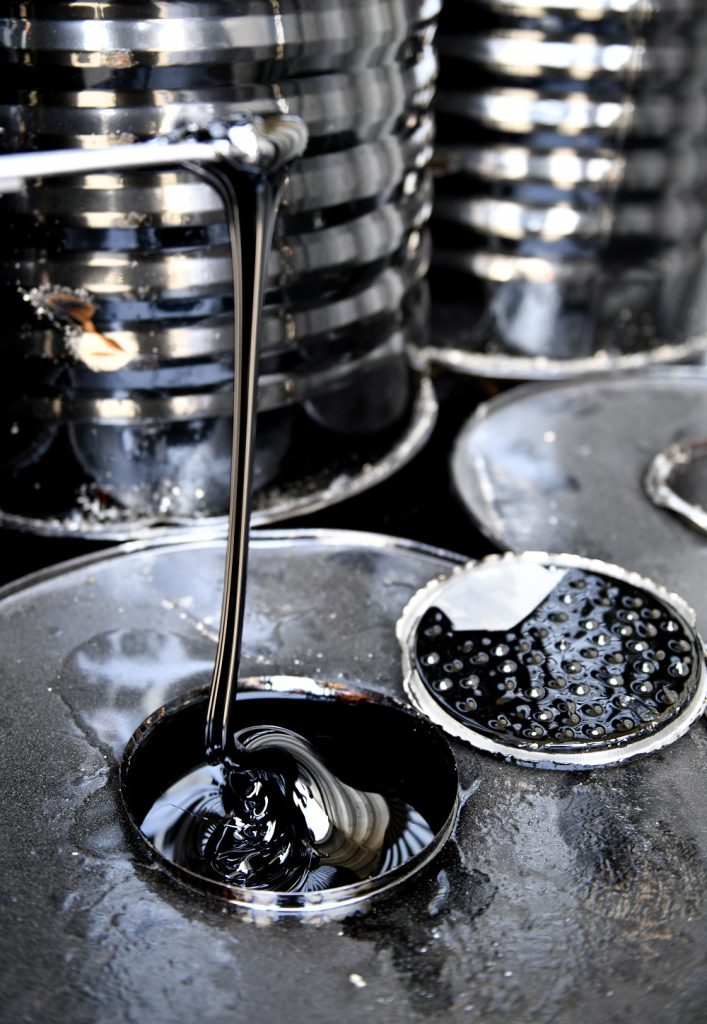


Bitumen Tests
Bitumen quality tests are a criterion for diagnosing the quality and classification of bitumen in the industry. These tests are also taken to control the quality and guarantee of the bitumen load issued and imported in the ports of origin and destination.
According to SGS standard, bitumen tests in summary, include:
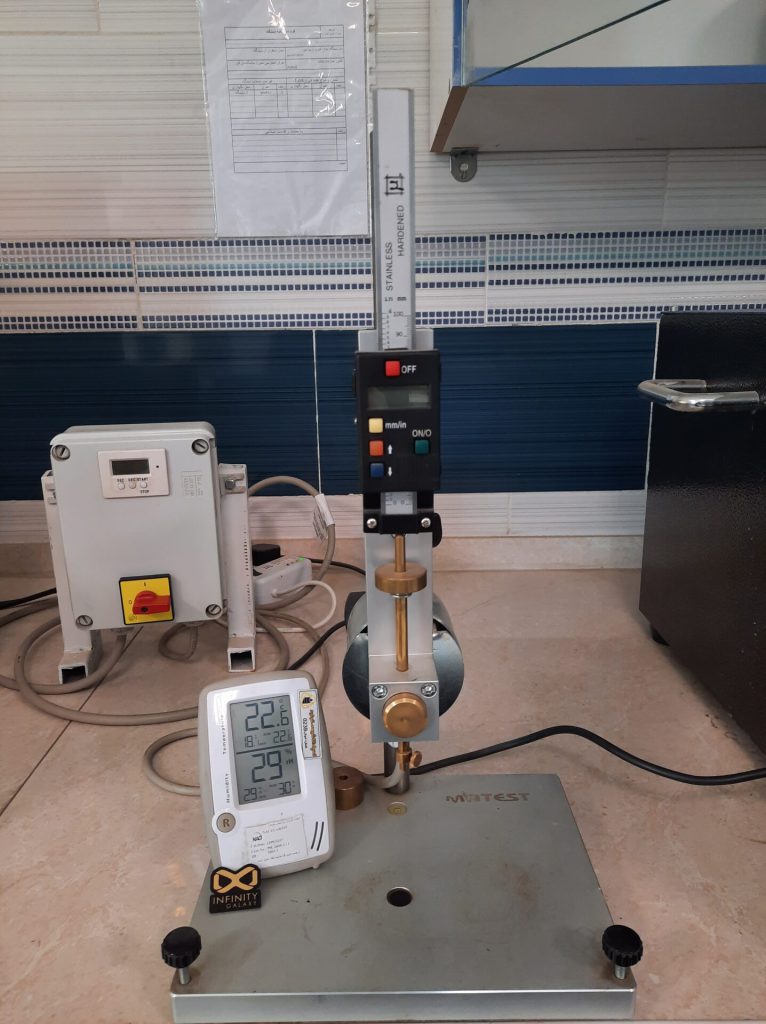
1- Penetration Test
The penetration test is used to measure the hardness and softness of bitumen. Penetration bitumen obtained from the refinery is classified based on this test. The degree of penetration of bitumen is directly related to its ductility and shows that asphalt has a higher loading capacity.
High penetration bitumen is suitable for cold climates and low penetration bitumen is suitable for hot climates.
To perform this test, a needle is penetrated into the bitumen surface with a load of 100 grams for 5 seconds. The degree of penetration is equal to the amount of needle penetrating. Its unit of measurement is 0.1mm.
To know more details, you can read the bitumen penetration test.


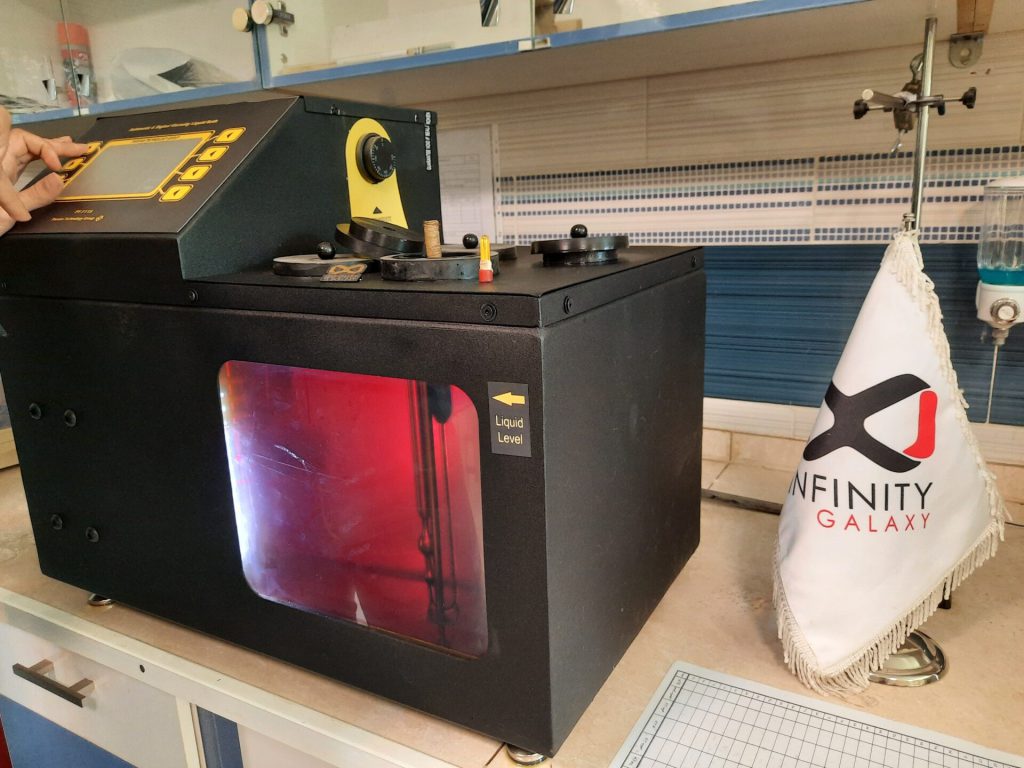
2- Viscosity Test
Viscosity test is used to determine the adhesion of bitumen to asphalt aggregates. Bitumen must have an optimal viscosity value. This means that very viscous or very low viscosity bitumen are not suitable for road construction. In addition, viscosity is highly sensitive to temperature increase, and with increasing temperature, the amount of viscosity decreases as a result, its cohesion is lost. For this reason, viscosity is measured at temperatures of 60 °C and 135 °C. By measuring these two viscosity we can have sufficient information about the best temperature we should mix and compact bitumen with aggregates.
To measure the viscosity, by the viscometer apparatus, the time required to remove a certain amount of bitumen from the viscometer is measured and multiplied by the correction factor of the device. The number obtained is equal to the viscosity of the bitumen.
To know more details, you can read the bitumen viscosity test.


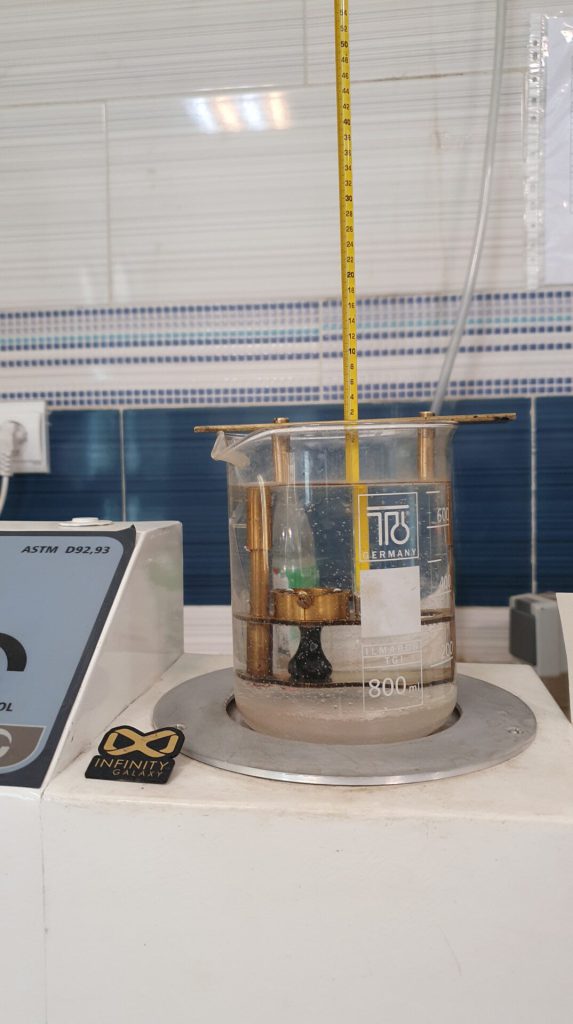
3- Softening Point Test
Bitumen as a combination of different hydrocarbon materials such as asphaltene and resin does not have a specific melting point. By heating the bitumen, it becomes soft and melts slowly.
The temperature at bitumen starts to melt/softer is called the softening point. This point is important for engineers because it indicates at what temperature the bitumen loosens and its adhesive decreases.
The laboratory method of measuring the softening point is the ring and ball method.
To perform the test, the bitumen sample is taken in two brass rings. Two steel balls are placed on the bitumen samples. Then the assembly is placed in a water bath and heated.
The softening point is the temperature at which the steel ball coated with bitumen hits the bottom of the glass beaker.
To know more details, you can read the bitumen softening point test.


4- Ductility Test
As long as the bitumen has good ductility, it will be resistant to road traffic as well as expansion and contraction of bitumen due to temperature changes, and the possibility of asphalt cracking will decrease and asphalt life will increase.
To measure this property, bitumen is poured into a special mold and the mold is pulled from both sides at a constant speed of 5 cm per minute. The amount of bitumen stretched to the moment of rupture is reported as ductility. The longer the length, the greater the ductility.
To know more details, you can read the bitumen ductility test.


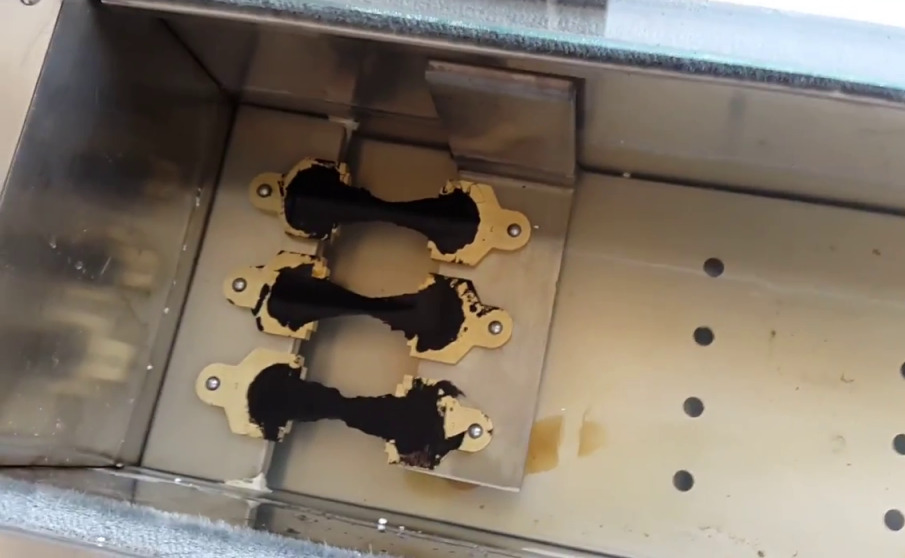

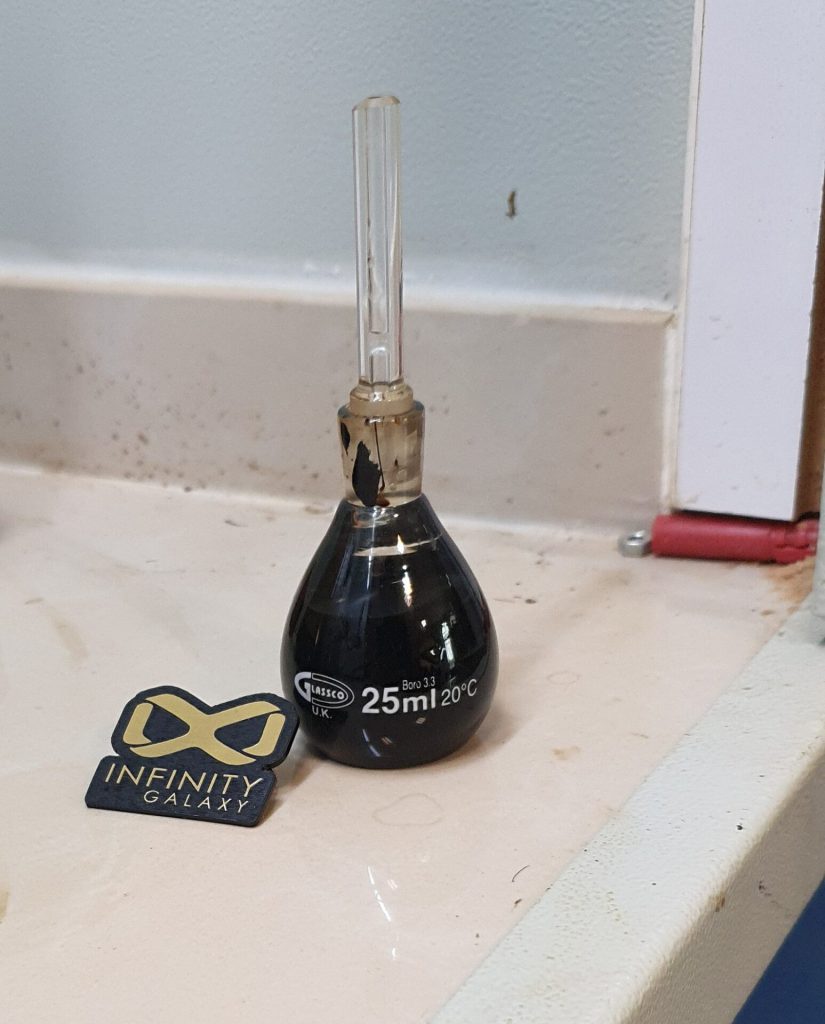
5- Specific Gravity Test
Specific gravity is the ratio of the mass of bitumen to the mass of water, while both of which have the same volume.
Each bitumen has a certain amount of specific gravity. As a result, this property is used to measure the amount of impurities in the bitumen. It is also used for calculations.
We use a pycnometer to measure this property. First, weigh the pycnometer, then fill it with bitumen and weigh it again. In the same way, fill the pycnometer with water and weigh it. We subtract the weight of the pycnometer from the readings of the pycnometer filled with water and bitumen. The ratio of bitumen weight to water weight is equal to the specific gravity of bitumen.
To know more details, you can read the bitumen specific gravity test.


6- Solubility in TCE
This test is performed to measure the purity of bitumen. This test detects non-oil impurities. For this purpose, 2 grams of bitumen is dissolved in 125 ml of trichloroethylene. The solution is weighed and then filtered through Whatman paper. Impurities are washed and dried and finally weighed. The percentage of impurities should not be more than 1% because it indicates the low quality of bitumen. High impurity in bitumen will have low adhesion strength.
Insoluble matter (%) = mass of insoluble materials / mass of bitumen sample
To know more details, you can read the bitumen solubility test.


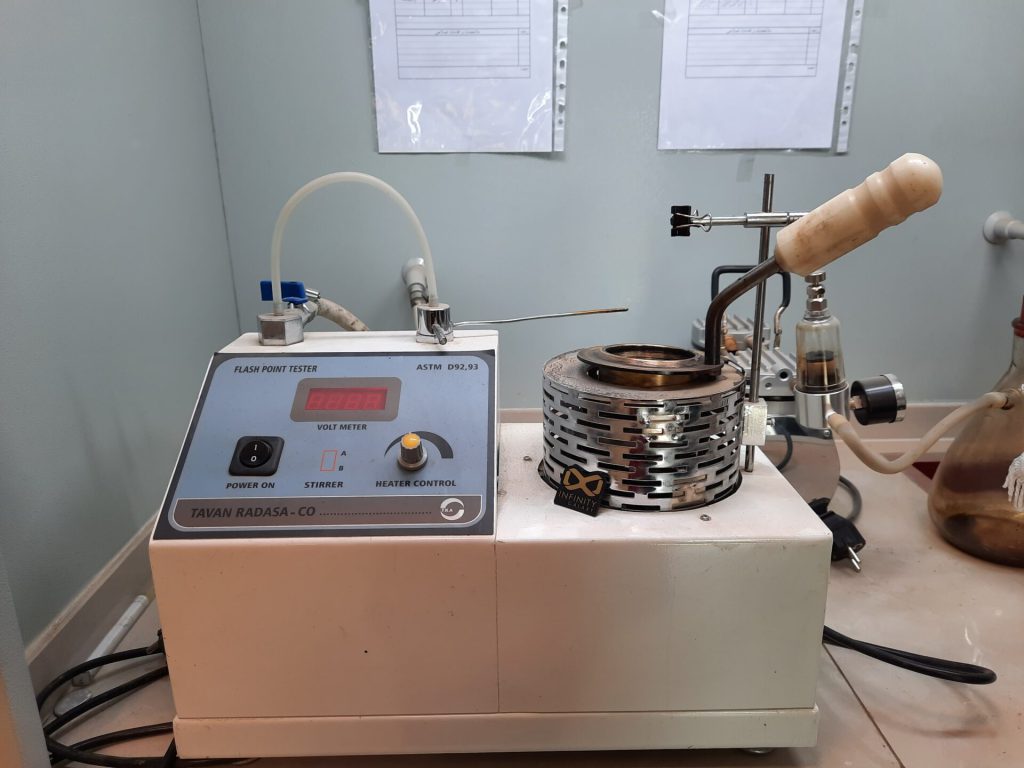
7- Flash and Fire Point Test
There are also risks in transporting and storing flammable materials. As a result, it is more important to notice the flash and fire point of bitumen.
Heat causes liquid materials to evaporate. If the liquid is flammable, it will catch fire if there is an ignition source like a flame.
Two devices are used to obtain the flash point and fire point:
- Pensky-martens
- Cleveland open cup tester
The procedure of the test is that bitumen is poured into the cup of the apparatus and then it is heated.
During heating, the flame passes over the liquid surface and through the vapors once every 2 seconds.
The temperature at which an instant flame appears on the surface of bitumen is called a flash point.
To obtain the fire point, heat is continued and the flame continues to pass over the surface of the liquid until an instant flame reappears on the liquid surface for a moment.
Compared to the previous flame, this one lasts longer. Its temperature is reported as the fire point.
To know more details, you can read the bitumen flash and fire point test.


8- Loss on Heating Test
The amount of volatiles in the bitumen is measured by the loss on heating test. Volatiles are compounds that have a lower boiling point than water and evaporate at a lower temperature.
The higher the percentage of volatile materials in the bitumen, the harder it becomes for the asphalt during the heating process and it loses its elasticity. A suitable bitumen binder should contain less than 1% volatiles.
To perform this test 50 g of bitumen sample is heated in the oven at 163 °C for 5 hours. After that, the bitumen sample is weighed.
The percentage of loss on heating is calculated as follows:
Loss on heating (%) = [(Initial weight – Final weight)/Initial weight]*100
To know more details, you can read the bitumen loss on heating test.
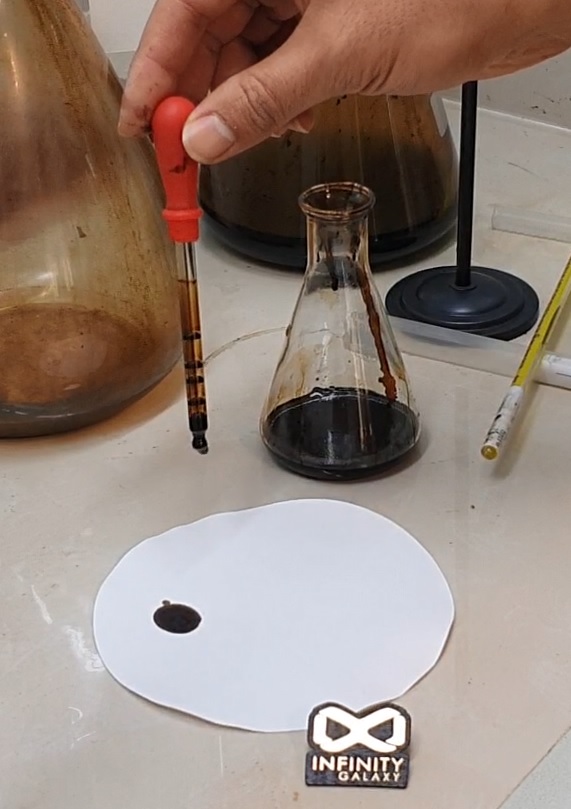
9- Spot Test of Bitumen
The spot test of bitumen is used to indicate that the bitumen is not damaged during the refinery’s overheating.
In a refinery, if the heating was so high the cracking occurs in bitumen. Cracked bitumen is not sticky enough to hold aggregates together. Moreover, it can not tolerate the preheated process for road construction.
To perform the test 10 ml of a solvent is put in a flask containing 2 grams of bitumen sample. The solution is rotated and placed in boiling water until it is dissolved completely.
After it cools at room temperature, put a drop on filter paper.
If the trace of the drop is brown the test is negative. Inversely if the drop is brown with a black center the test is positive and the bitumen is damaged.
To know more details, you can read the bitumen spot test.


10- Drop in Penetration after Heating Test of Bitumen
Drop in penetration tests measure the hardness and volatile content of bitumen.
When bitumen is heated for construction the volatile component evaporates and causes the material to harden. When bitumen has more volatile content, its hardness increases after heating.
To perform the drop in penetration after the heating test, apply the needle with a load of 100 grams for 5 seconds on the bitumen surface. Note the amount of penetration in 0.1 mm.
Then the bitumen sample is placed in the oven at 163 ͐degrees celsius for 5 hours.
After removing the sample, it is allowed to cool. In the next step, the penetration test is repeated.
Drop in penetration value (%) =
[ difference between 2 amount of peneration/initial amount ] * 100
To know more details, you can read the bitumen drop in penetration test.
Bitumen Manufacturers
According to global statistics, China is the largest producer (and also consumer) of bitumen in recent years, with a production of 22 million tons per year, and the United States is in close competition with an annual production of nearly 21 million tons. Russia ranks third with a production of almost 7.8 million tons per year. Iran, India, and South Korea follow closely behind with annual production of about 5 million tons,
It is important to mention that the most important exporters are South Korea, Iran, Singapore, Russia, Canada, and Germany respectively.
In the bitumen market, competition is easier for manufacturers and sellers than in other markets.
There are no major players in this market. The top 5 largest producers and marketers of bitumen are:
- Exxon Mobil Corporation
- Royal Dutch Shell Plc
- bp p.l.c.
- Nynas AB
- China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (SINOPEC)
If you are interested in knowing more about bitumen manufacturers in the world, read “Top 6 Bitumen Manufacturers in the World”.
Annual Consumption of Bitumen
Bitumen consumption has been steadily increasing from the beginning of 2000 to 2020.
The most common industry in which bitumen is used is the road construction industry. Demand for bitumen is close to 100 million barrels per year, which is due to the expansion of:
- Communication roads and repair of old asphalt to increase their service life
- Construction has led to an increase in roofing
- Various industries and civil works such as dam construction around the world in which bitumen is used
The most influential factors that affect the global demand for bitumen each year are:
- Economy
- The government budget for the road
- Natural disasters such as rapid landslides, floods, volcanoes, and so on.
- An unplanned event like terrorism, accidents, or corona!
The largest consumer of bitumen in the world is Asia-Pacific, where its main consumptions are in China due to the expansion of environmentally friendly construction projects, and India due to the extensive road network improvement project.
After Europe, in third place comes North America, whose main consumers are the United States, followed by Canada.
The lowest volume of bitumen is consumed in African countries.
The amount of bitumen consumption in 2020 was over 100 million cubic meters. This number could have been higher, but due to the coronavirus pandemic and quarantine, many development projects were stopped, especially in early 2020.
In 2021, with the spread of two waves of the COVID-19, the demand for bitumen decreased cross-sectionally. َAlthough due to the expansion of vaccination and the controlled situation the construction and industrial projects in the world gradually grew and the consumption of bitumen increased.
Consumption is expected to decrease to less than 4% from 2022 to 2026. This forecast is due to the reduction of road construction projects using bitumen. One of these projects is the production of environmentally friendly roads in China.
Effects of Bitumen on Health
There are always concerns about the use of chemicals and the risks associated with their harm to health or the environment.
Even though bitumen is not a highly toxic substance, safety precautions must be observed when using it, especially for workers who work with it continuously. They need to observe the following points:
- Wearing appropriate work clothes. Work clothes must have long sleeves and pants
- Use thermally insulated gloves
- Use vented goggles when working with liquids
- Use a face shield when working with corrosive and toxic substances. The use of vented goggles is also recommended for extra protection
- If they are exposed to toxic foam, it is necessary to use a mask
–Bitumen Health Effects Include:
- Heated bitumen vapors lead to coughing, a scratchy throat, headaches, skin rashes, fatigue, eye irritation, and lung problems
–Long-Term Side Effects Include:
Bitumen exposure can cause lung and stomach cancer, pigment changes in the skin, bronchitis, and emphysema. In addition, bitumen additives may cause damage to the liver, kidneys, and nervous system.
When hot bitumen releases hydrogen sulfide gas into the air, suffocation and even death may occur.
Because bitumen is a highly flammable material, care must be taken to keep energy sources such as cigarette butts, flames, and’s away from work.
Impacts of Bitumen on the Environment
By heating bitumen in road construction, toxic vapors enter the atmosphere. Furthermore, The evaporation of bitumen occurs at air temperatures, especially in the summer. This results in air pollution.
Asphalt also reduces soil fertility. In fact, natural soil elements such as iron and calcium, which are essential for plant growth, are reduced. To solve this problem and increase productivity, chemical fertilizers with safe concentrations can be used.
It is also better to use environmentally friendly packaging in the transportation of bitumen. Because by transporting thousands of barrels of New Steel drum, a large amount of waste enters the environment. Which has high recycling and reuse costs. It is better to use compatible packages such as jumbo bags.
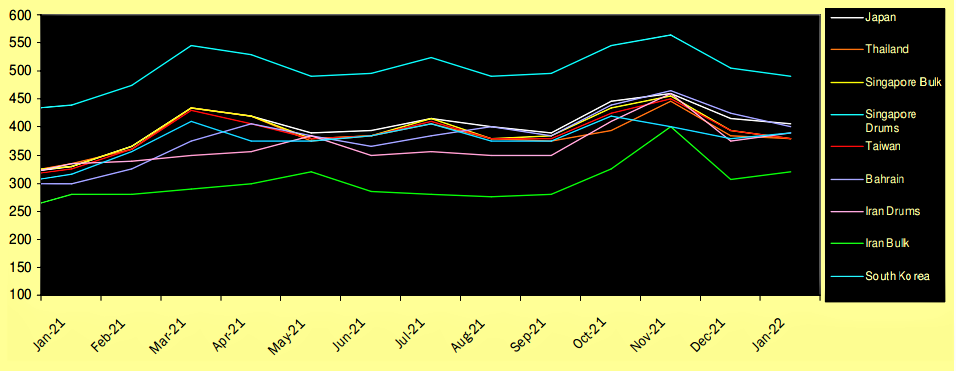
Bitumen Price
The price of bitumen depends on several factors. The main factor in changing the bitumen price is the price of crude oil and the amount of supply and demand in the market.
In early 2020, oil prices and, of course, bitumen prices plummeted due to the coronavirus epidemic and quarantine conditions, as construction and industrial projects stalled and demand decreased.
In 2021, the price of bitumen fell cross-sectionally due to two Corona variants, Delta and Omicron. If world conditions are stable, in 2022 prices are expected to rise with a slight slope.
In the Middle East, the main suppliers of bitumen are Iran, Iraq, and, Bahrain. Factors affecting the price of bitumen in the Middle East are:
- World oil prices
- Regional prices of sulfur fuel oil
- The amount of demand from consuming countries, especially India
- Exchange rate of the Rial against the dollar
- Prices of global competitors such as Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, Italy, Greece
- Political conflicts, especially political conflicts in the Persian Gulf area in the Middle East
- Corona condition and its direct impact on demand and project progress
- Shipping cost
- Local competition between refineries
The above factors can also affect the global bitumen price.

Storage, Packaging and Shipping Conditions
Bitumen has many packages depending on whether it is solid or liquid. These packages include:
Bitumen is a flammable viscous material; so its packaging is very important considering the factors like cost, environment, storage, and shipping.
Drum packaging is the most common packaging because it is available in different sizes, has higher security, and is easy to transfer.
It varies depending on bitumen volume, height, thickness, and lid. Although new steel drums are preferred to bulk trade, they are still more expensive compared to jumbo bags (steel is more expensive than plastic).
You can read more details on the “Bitumen Packages” page.
Bitumen Expiry Date
Bitumen expiry date depends on the type and grade of bitumen.
The properties of pure bitumen like penetration grade (Pen grade), viscosity grade (VG grade) and performance grades (PG grade) in storage for a long time will not be changed. Generally the stability of these grades of bitumen is high.
But for liquid bitumen like bitumen emulsion or cut back bitumen, the properties can be changed in the storage. The penetration bitumen, viscosity bitumen and performance bitumen have a long shelf-life, 3 to 15 years, but bitumen emulsion and cut back shelf-life is approximately 6 months.


