A specific gravity test measures how much lighter or heavier bitumen is compared with the same volume of water. There are two methods to calculate the specific gravity of bitumen, the Pycnometer method and the Balance method.
The specific gravity of pure bitumen is in the range of 0.97 to 1.02. The specific gravity of tar is approximately 1.20.
When the specific gravity is less than 1 it shows the bitumen is lighter than water and when the value is more than 1 it indicates the bitumen is heavier than water.
Specific Gravity Value < 1 => Bitumen is lighter than Water
Specific Gravity Value > 1 => Bitumen is heavier than Water
Bitumen tends to float on the water surface more when the value is less than 1. Also, it tends to settle down when the value is more than 1.
Below is a video introducing you to the specific gravity test and its steps.
Following is a table of specific gravities for different penetration grades of bitumen based on ASTM D70:
| Specific Gravity of Penetration Grade Bitumen | ||
|---|---|---|
| Penetration grade bitumen | Specific gravity @ 25°C | |
| min | max | |
| 30/40 | 1.01 | 1.05 |
| 40/50 | 1.01 | 1.05 |
| 60/70 | 1.01 | 1.06 |
| 85/100 | 1.01 | 1.05 |
| 100/120 | 1.01 | 1.04 |
Why is Specific Gravity Test of Bitumen Important?
A specific gravity test can be used to classify bitumen. It helps to identify the type of bitumen. For example, bitumen 80/100 has a different specific gravity value from bitumen 30/40.
Also to control the quality of bitumen we use its specific gravity. By using that, the impurity of bitumen is recognizable. Because impure bitumen has higher specific gravity.
For road construction, bitumen is used with aggregates. To have a suitable and stable asphalt, the optimal volume of bitumen must be used. Because too much bitumen makes asphalt sticky. In addition, when there isn’t enough bitumen, the aggregates don’t stick together.
The bitumen binder should coat the space between the aggregates well. For this reason, we need to calculate the density of voids.
The volume of voids is determined by the density of bitumen and the density of aggregates.
These calculations are performed using Marshal Mix Design.
The volume of bitumen is necessary for Marshal Mix Design. However, the volume is converted to mass when we mix the bitumen and aggregates. Because measuring weight is easier than measuring volume.
Weight = Specific Gravity * Volume
International Standard Methods for Specific Gravity Test of Bitumen
Various standard methods are provided to determine the specific gravity of bitumen, as follows:
- ASTM D 70
- AASHTO T 228
- IS 1202
- EN 15326
- IP 549
The Apparatus Components and Test Steps of Specific Gravity
In the following, we describe the procedure of calculating specific gravity based on two methods:
- Pycnometer method ( ASTM D70 )
- Balance method ( IS 1202 )
1. Pycnometer Method
Apparatus
- Specific gravity bottle (pycnometer): The ordinary specific gravity bottle shall be used for materials that remain fluid at 25 °C. On the other hand, the wide mouth capillary type shall be used for materials that remain semi-solid or high viscous at 25 °C.
- Oven
- Heater
- Water bath
- Thermometer
- Electronic balance


Procedure
Wash the specific gravity bottle (pycnometer) and dry it in the oven. Weigh it with its stopper. Consider the value as A.
Fill the pycnometer with distilled water and insert the stopper. Put it in a water bath at 25 °C degrees and wait for it to warm. Then take the pycnometer out of the water bath and dry it with a towel. Record the weight with the balance and consider it as B.
Heat the bitumen between 75 °C and 100 °C to become completely liquid. Fill half of a clean and dry pycnometer with bitumen. Be careful that air does not enter the sample.
Allow it to cool at room temperature. Then place in a water bath at a temperature of 25 °C to reach the bath temperature. Dry it completely, then weigh it and consider the value as C.
At the next step, fill the other half of the bottle with distilled water. Place it in a water bath at a temperature of 25 °C to reach the same temperature as the water bath. Dry it and weigh it. Consider the value as D.
Finally, the mass of the pycnometer, which is filled with bitumen, is measured. Consider that value as E.
Use the following formula to calculate the specific gravity:
For solid and semi-solid bitumen:
Specific gravity= (C-A)/[(B-A)-(D-C)]
For liquid bitumen:
Specific gravity=(E-A)/(B-A)
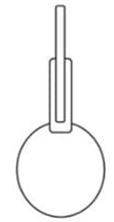
A= mass of pycnometer
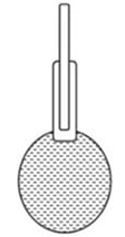
B= mass of the pycnometer is filled with water
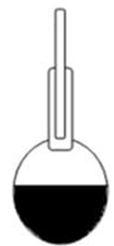
C= mass of pycnometer about half-filled with the bitumen
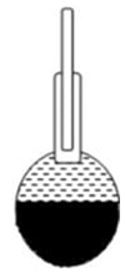
D = mass of the pycnometer about half-filled with the material and the rest with distilled water
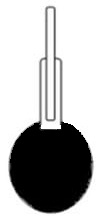
E = mass of the pycnometer filled with the bitumen.
2. Balance method
Apparatus
- Balance straddle: It has a pan straddle with a suitable size to support a beaker. It should be suitable to determine the weight of the specimen in water.
- Analytical balance scale
- Thermometer
- Waxed silk thread
- Cubic brass mould
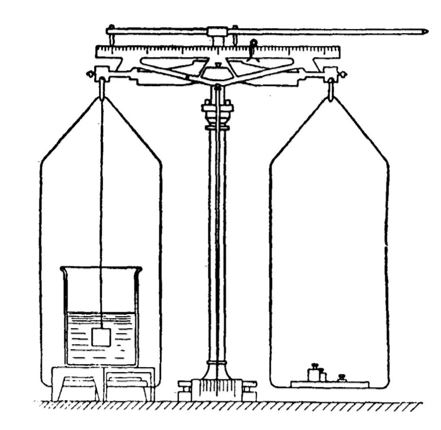
Procedure
a) Sample preparation:
Heat the bitumen sample gently. Coat the cubic mould brass with a mixture of glycerine and dextrin.
Pour the specimen into the mould and fill it. It is better to fill it in a little more than needed. Then cut the excess amount with a hot knife.
Let the specimen cool at room temperature. After that, remove it from the brass mould.
b) Test:
Hang a piece of wax silk thread from the balance and tie it. The length of the thread should be long enough to reach the pan.
Attach the sample to the thread and weigh it.
As the sample is suspended from the thread, place it in a water bath at 25 °C and weigh it.
Calculate the specific gravity of the material as
follows:
Specific gravity = A/(A-B)
A = mass of the dry specimen
B = mass of the specimen when immersed in distilled water.