During the heating of flammable or combustible material, vapor is generated near its surface. The flash point test measures the lowest temperature at which the vapor burns in the presence of an ignition source with an instant flame.
The fire point test measures the temperature higher than the flash point. At the fire point, the flame lasted more than 5 seconds.
Note: In accordance with the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), flammable liquids have a flash point of below 100 °F (37.2 °C), and combustible liquids have a flash point of equal to or above 100 °F (37.2 °C).
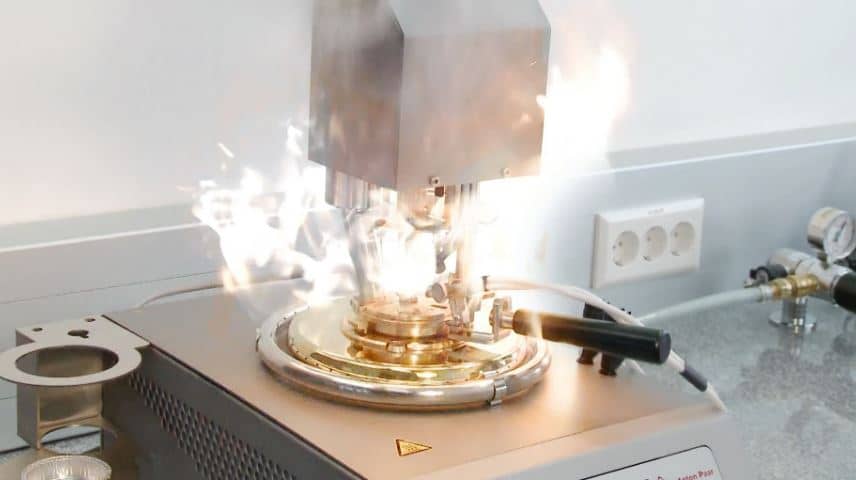


“Cleveland open cup tester” and “Pensky-martens” are two famous apparatus used to measure the flash and fire point of bitumen.
These apparatuses are suitable for all types of bituminous materials with a flash point between 79 °C – 400 °C.
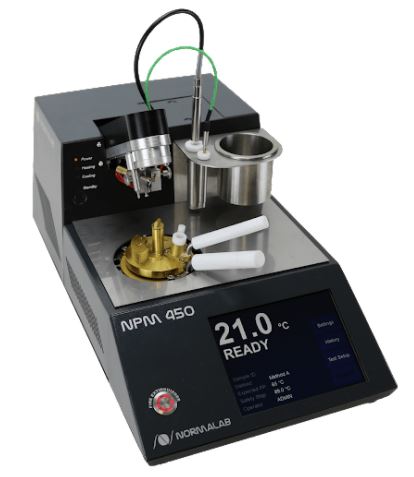




The test is started by pouring the sample into the test cup. The sample temperature rises. At the flash point temperature, the sample vapor is fired by using a test flame. To determine the fire point, continue heating the sample until a flame appears above it. The flam must last for at least 5 seconds.
Following is the table of flash points of different viscosity bitumen grades based on Indian bureau standards (IS 1448) :
| Flash Point of Viscosity Bitumen | |
|---|---|
| Paving grades | Flash point ( °C) by (Cleveland open cup) |
| VG 10 | 220 °C |
| VG 20 | 220 °C |
| VG 30 | 220 °C |
| VG 40 | 220 °C |
Why is the Flash and Fire Point Test Important?
Bituminous materials are flammable. Therefore, their applications, storage, and handling are always risky. Thus knowing flash and fire point is important to decrease the possibility of fire and enhance safety.
Standard Methods for Flash and Fire Point Test of Bitumen
Various standard methods are provided to determine bitumen flash and fire point, as follows:
- ASTM D 92
- ASTM D 93
- ASTMD 3143
- ASTM D8254
- AASHTO 48
- AASHTO 79
- EN ISO 2592
- IS 1448
- IS 1209
- IP 113
- IP 170
According to ASTM D 92, the flash and fire point tests are conducted as follows:
Flash and Fire Point by Cleveland Open Cup Tester:
– Component:
- A brass test cup
- Heating plate
- Bead: It is placed on top of the device. Consequently, it is possible to compare the flame size.
- Temperature regulator: To control the heater
- Test flame applicator: The device for applying test flame. It has a hole and is swung left to right and right to left. It is positioned 2mm above the plane of the rim of the test cup.
- Thermometer
– Procedure
This test is suitable for all types of bitumen. A solid bitumen sample should be heated up until it becomes completely liquid. Bitumen must not be heated at high temperatures. The proper temperature for heating is approximately below the expected flash point.
Fill the clean and dry test cup until the filling line level. If the level of bitumen is more than the filing line, the excess material must be removed by syringe or pipette.
Be careful that the surface of the bitumen sample is without any bubble; otherwise, the test fails.
Place the thermometer vertically in the test cup. Then fire the test flame.
Apply the heat with the help of the regulator. The temperature rise rate of the sample should be 5-17 °C per minute.
If the material has a low flash point or is highly viscous, a heating rate of 5 to 6°C per minute is recommended from the beginning of the test to the end.
When the test temperature is approximately 56 °C lower than the expected flash point, turn down the heater. To continue the test, the rate of rising temperature of the sample should be between 5 and 6 °C per minute.
At 28 °C below the expected flash point, apply the test flame to move. Every time the sample temperature rises by 2 °C, the test flame must pass over the sample.
Record the temperature at which the fire appears instantly above the bitumen surface. Then use equation 1 to calculate the flash point.
Once you reach the flash point, continue to heat the sample to determine the fire point. The sample temperature should be increasing at a rate of 5 to 6 °C per minute.
Record the temperature at which the flame appears over the surface of bitumen and maintain at least for 5 seconds. Then to calculate the fire point use equation 1.
Flash or fire point =C+ 0.033*(p-760) (1)
Where:
C = The temperature obtained by the test,°C
P = Ambient pressure which is recorded by barometer, mm Hg
Note: In repeated measurements for each sample by the same apparatus, the maximum difference between the highest and lowest readings shall be less than 8 °C.
If you are interested in reading about other tests of bitumen, take a look at the bitumen tests.
FAQ
What is the difference between flash point and fire point?
The difference between flash point and fire point is that the flash point is the lowest temperature at which a petroleum product produces flammable vapor which ignites by passing a flame over it. The flash point is temporary and will not continue when the source of flame is removed. But the fire point is the temperature that, after passing the flame over it, starts to burn continuously. The fire point temperature is higher than the flash point.
Is bitumen flammable?
Yes. Bitumen is a flammable product that ignites if overheated.