Generally, there are 4 different ways of producing bitumen. These methods are Straight Run, Air Blowing, Deasphalting, and Blending.
Air Blowing is the most common way.
Let’s take a look at the process of bitumen production in this article. Before that, read the infographic and watch the video below to get a better understanding of bitumen production.
What kind of crude oil is suitable for producing bitumen?
The raw material for producing bitumen is derived from crude oil. But which type?
Crude oil with a specific gravity greater than 0.9 is suitable for producing bitumen. Because they have a suitable amount of heavy molecules. They include asphaltene and maltene which have a key role in bitumen production. Please refer to the following of this article for more explanations.
Generally, oil with such characteristics has the potential to produce 20-50% bitumen.
Also, these crude oils have a sulfur content of more than 1 weight percentage. Sulfur has a key role in polymerization and raises the viscosity of the bitumen.
Note: Sometimes proper crude oil is obtained by blending different types of them.
What is Bitumen Made of?
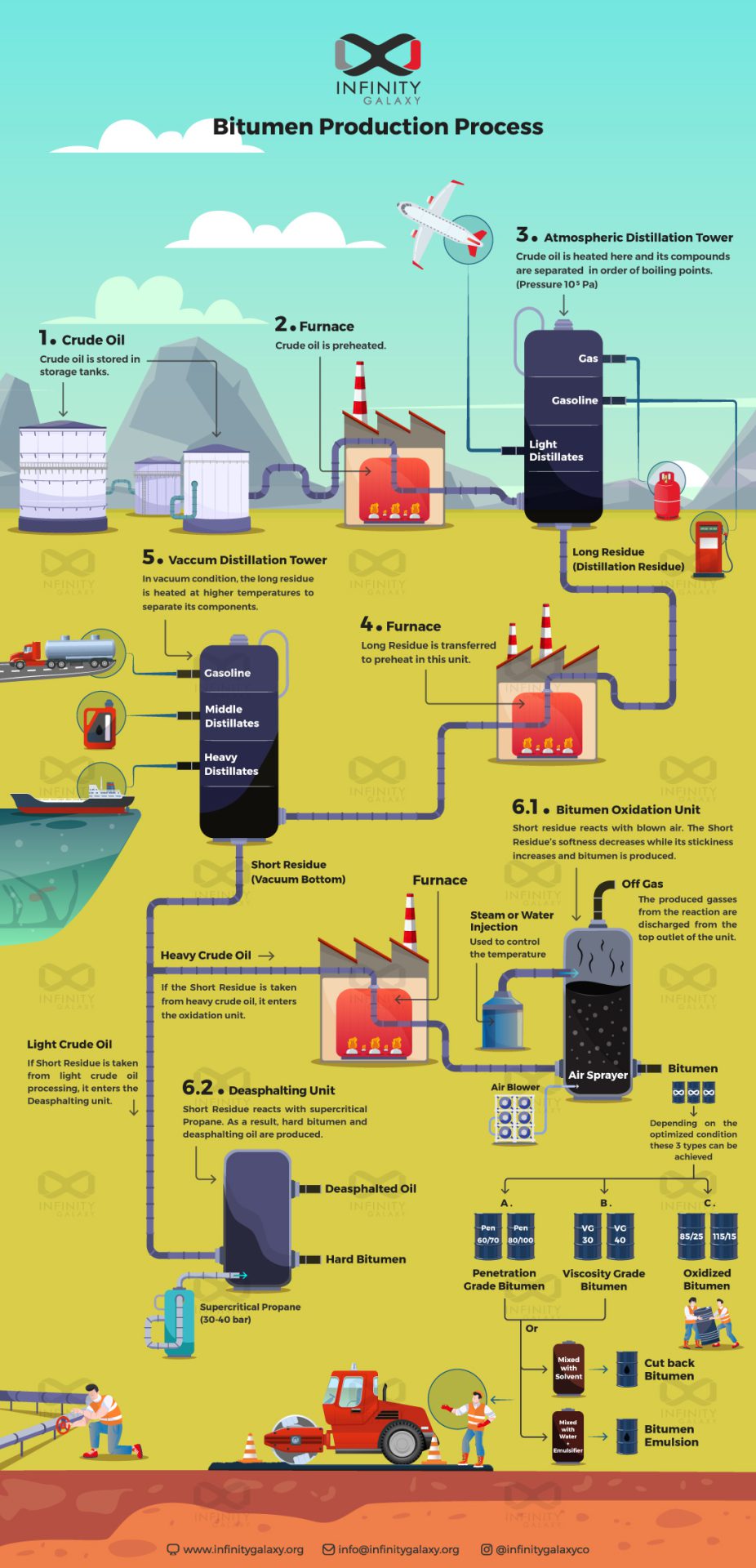
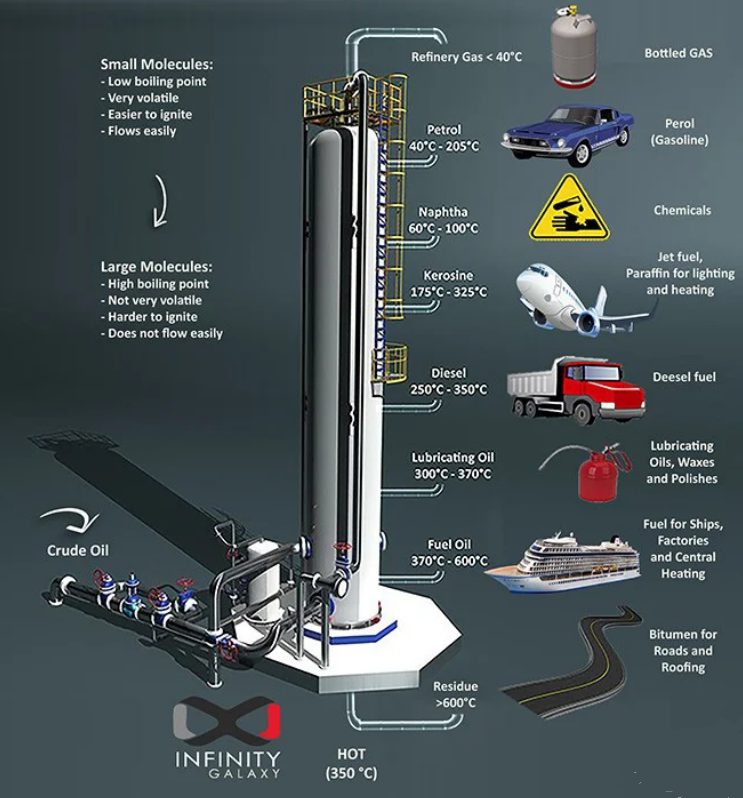
As mentioned before, bitumen is obtained from crude oil. Crude oil is a mixture of different materials which have different boiling points. As a result, for the separation process, distillation towers are used.
Crude oil enters the tower and is heated.
Heating leads to the separation of crude oil components in order to their boiling point. In general, components with lower boiling points separate sooner. The vapors of these lighter components are collected in specific trays placed at various heights in the distillation tower.
The heaviest components with high boiling points remain at the bottom of the distillation tower.
There are two types of distillation towers:
* Atmospheric: Crude oil is heated in the presence of atmospheric pressure.
* Vacuum: The residue of the atmospheric tower is heated below atmospheric pressure (near-vacuum condition).
The residue of the atmospheric distillation tower is called the long residue.
Long residue can not be heated at very high temperatures. Heating causes a reaction between oxygen and long residue then coke is produced.
As a result, it is taken to the vacuum distillation tower to produce more products at higher temperatures without damaging long residue.
Bitumen is produced from the residue of a vacuum distillation tower. It is called short residue or vacuum bottom.
Occasionally, the long residue or a combination of different short and long residues is also used.
It should be noted that a suitable penetration for short residue or vacuum bottom is between 35-300 dmm (deci-millimeter).
Bitumen Production Methods
There are several processes for producing bitumen that are described below.
1-Straight Run
Sometimes vacuum bottom or short residue has the bitumen property. It means that it has reasonable penetration and viscosity.
It directly can be used as bitumen, especially in paving work.
But most often, vacuum bottoms need to go through different production stages.
2-Air Blowing
The primary way of producing bitumen is air blowing. This process includes different ways that are explained in detail in the following.
In this method air at the desired and almost constant temperature range blows through the feedstock (vacuum bottom).
The aim of air blowing is to produce Asphaltene molecules, which increase the viscosity of the bitumen.
Air blowing results in the generation of Ester molecules which leads to the generation of larger molecules (polymerization process).
Oxygen atoms bond two different molecules. As a result, heavier molecules and asphaltene are generated.
Oxygen molecules react with the vacuum bottom. This causes the bond between Hydrogen and Carbon atoms to be separated and cyclic molecules to be generated (hydrogenation process).
During air blowing, the penetration of the vacuum bottom is decreased, and/or its softening point is increased.
Blowing is done in different ways, which are explained below.
A) Semi-Blowing or Air Rectification
The semi-blowing process can be applied in two methods; Batch blowing or Continuous blowing.
- Batch Blowing
In this process, a certain volume of feedstock must be heated before entering the reactor.
Depending on the degree of penetration and viscosity of the demanded product, blowing lasts between 3 to 24 hours.
During air blowing, oxidation reactions occur which lead to an increase in temperature. As a result, a cooling system is used in the tower to keep the temperature constant.
- Continuous Blowing
In Continuous blowing, the vacuum bottom enters the reactor with a constant flow rate.
The blowing temperature in the reactor is constant in a particular range.
The temperature of the fresh feed is lower than the operating temperature. But the heat of the blowing process and oxidation reaction causes the bitumen to heat up.
The advantages of the continuous method over the batch process are:
- Increasing the production of bitumen per unit of time.
- Reducing the preheating cost of the vacuum bottom before entering the reactor.
- Due to its continuous nature, it is easy to control and process.
B) Fully Air Blowing
In a fully blown process, the air is blown through the feedstock more than in the semi-blown method.
It applies upon a blend of a vacuum bottom with a relatively low viscosity property to reach oxidized bitumen.
The amount of blowing that is required, depends on the temperature in the column and the air-to-feed ratio.
3-Solvent Deasphalting
One of the methods of bitumen production is to modify the vacuum bottom in propane deasphalting units.
In these units, the vacuum bottom is mixed with propane (sometimes butane) then de-asphaltene oil is extracted from it.
At the end of the process, the remaining product is bitumen.
There are some differences between this bitumen and refined bitumen from the same feedstock.
Propane deasphalting causes the reduction of residue further. Also, dependent on crude oil properties, this method can produce a bituminous product that has:
- Lower viscosity
- Higher ductility
- Better temperature resistance than other bitumen
Usually, this process is used on crude oil with a low content of heavy molecules.
4-Blending
Blending is not the direct method of producing bitumen. However, sometimes, it is used to achieve bitumen with desired properties.
Several types of bitumen are mixed together in order to obtain bitumen with the preferred properties.
For example, penetration bitumen 40/50 is combined with penetration bitumen 200/300 to obtain the desired bitumen with a similar penetration to bitumen 80/100.
Check out Below links to learn More about:






4 comments
Lennox Lewis
Very nice work done by these great people as it easy to learn from this piece of an article
Tony Aleoegena-Raphael
Really nice work on bitumen from crude oil. I wish you could do the same for neutral occurring bitumen. We have a large deposit in Nigeria and would like to process it for local and export markets.