Bitumen emulsion is a liquid mixture that contains bitumen, water, an emulsifier and some additives.
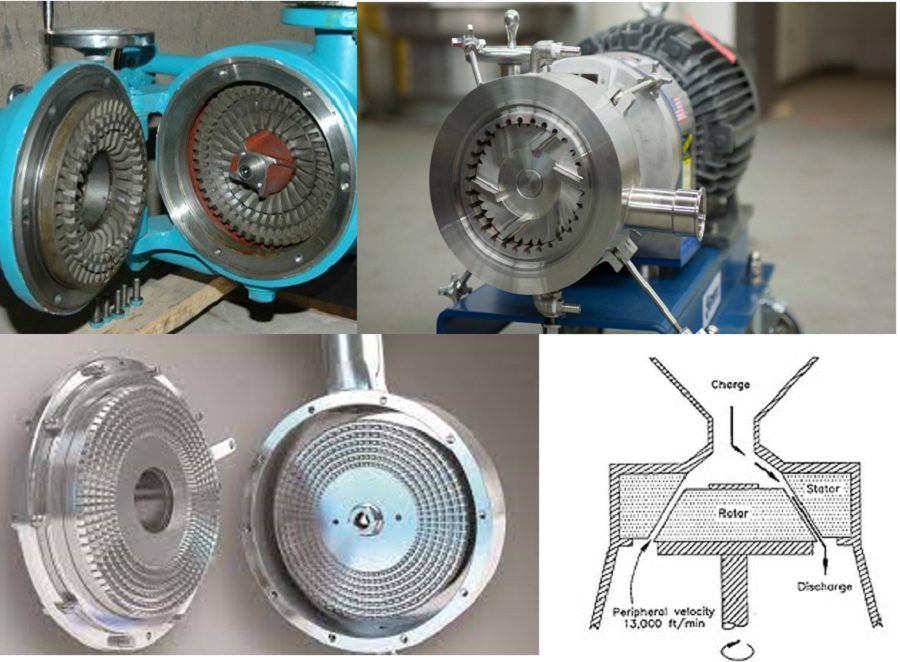
Mixing bitumen and water occurs through a particular mill called a colloidal mill. It breaks the bitumen into fine droplets.
As a result, it makes it easier for the emulsifier molecules to reach the bitumen droplets to suspend and disperse them in water.
This article provides an overview of bitumen emulsion production.
The bitumen and water phases must first be prepared to produce bitumen emulsion. This preparation is done for easy transferring and mixing.
1- Bitumen preparation
Emulsion bitumen consists of 50 to 70% bitumen. Generally, the bitumen is penetration grade 60/70, 70/100, 100/130 or Vg 30 grade of viscosity bitumen.
The suitable bitumen for emulsion production should be soft and have a viscosity of less than two poise. Sometimes bitumen needs to be heated to reach these conditions.
Read Viscosity Test of Bitumen Methods.
But why should bitumen have these characteristics to produce bitumen emulsion?
a) To easily transfer and pump bitumen from vessels to the mill, bitumen viscosity should be less than two poise.
Low viscosity also allows bitumen and water to mix better.
b) The bitumen should be soft enough to break into fine pieces when milling.
2- Preparation of the aqueous phase
A bitumen emulsion typically contains 30-50% water phase.
In the aqueous phase, an emulsifier and other additives are dissolved.
The emulsifier contains 1% of the aqueous phase weight. It can be used in liquid or solid phases.
Sometimes water needs to reach a specific temperature to dissolve solid emulsifiers, which are available in plates, granules, etc.
Generally, the water temperature should be below 70 degrees Celsius because further increases lead to water evaporation.
As a result of evaporation, the water concentration decreases. Inversely, the emulsion concentration increases.
This changes the properties of the water phase and, as a result, the emulsion bitumen.
Cationic emulsifiers are usually created by mixing amines with water and acids. The preparation of anionic emulsifiers such as fatty acids requires the dissolution of a base (like caustic soda).
Read about Cationic Bitumen Emulsion.
3- Mixing Bitumen with Water to Make an Emulsion
In emulsification, bitumen is combined with water phase solution (emulsifying solution) by a particular bitumen emulsion mill or colloidal mill.
The colloidal mill consisted of two parts: a fixed part (stator) and a rotating part (rotator).
The rotating part rotates at 1000 to 6000 rounds per minute (rpm) and separates bitumen into fine droplets.
The rotating part is inside the fixed part. A 250 to 500 microns gap is between them.
Bitumen droplet size can be modified by adjusting the gap between the two parts of the mil.

Depending on the design and the amount of production, it is possible to mix the water phase and bitumen in three different ways and obtain bitumen emulsion.
The bitumen emulsion production method can be batch, semi-continuous or continuous.
A) Bath production
This method is used when the production quantity is small.
Based on the bitumen emulsion production requirements, an appropriate amount of bitumen and aqueous solution is determined.
The emulsifier solution and bitumen are stored in two separate reservoirs.
Then they are transferred into the colloidal mill by a pipe and a pump. Finally, the bitumen emulsion is produced by mixing them through the colloidal mill.
B) Semi-continuous production
In the semi-continuous method, the colloidal mill constantly rotates.
The water phase and bitumen phase have two reservoirs separately.
Bitumen and aqueous reservoirs deliver feed to the mill, while two full reservoirs store bitumen and water.
When the delivering reservoirs are empty, the full reservoirs begin transferring materials.
Bitumen and water are refilled into the two emptied reservoirs.
In this method, there are always full reservoirs.
C) Continuous production
In the continuous method, the colloid mill works smoothly.
Bitumen, water, the emulsifier and acid are transported separately by pipelines.
Before reaching the mill, all flows of materials enter a flow pipe. They are mixed in one stream and then enter the colloidal mill.