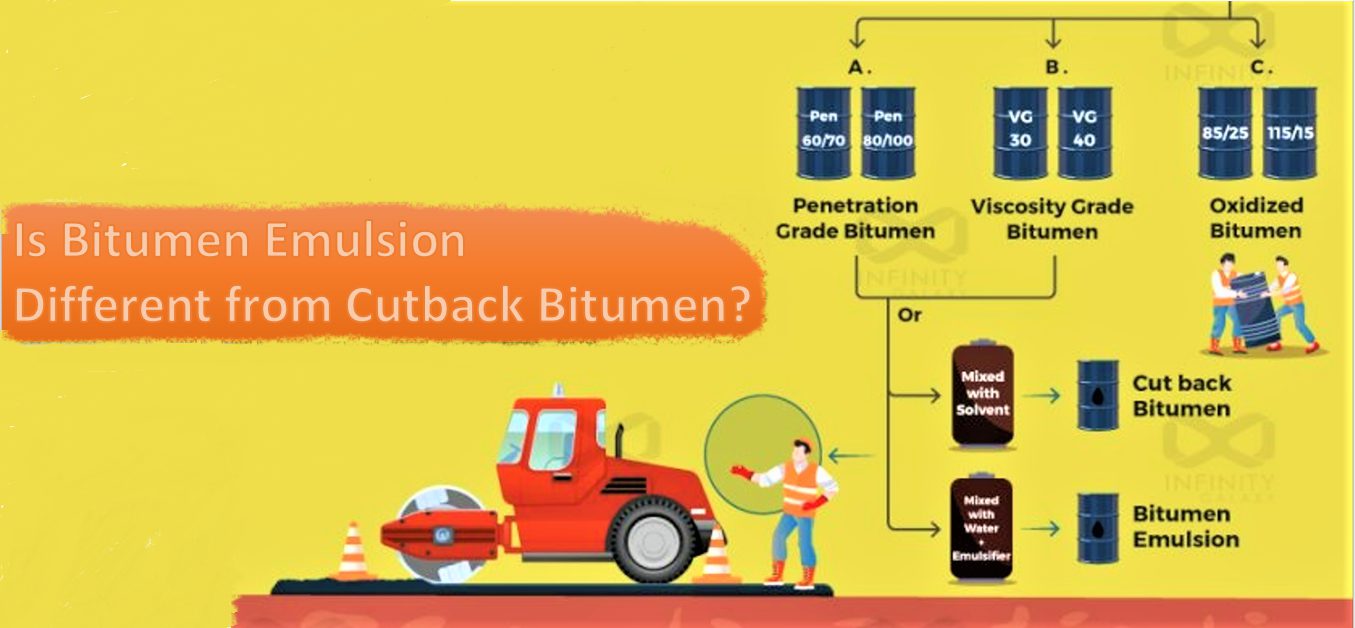
The cationic bitumen emulsion is a stable mixture of fine droplets of bitumen dispersed continuously in water by a chemical material called cationic emulsifier.
Compared to other bitumen emulsions, cationic bitumen emulsion is more widely used around the world. It is used for surfacing, cold mix asphalt, and road construction.
Let’s become deeper into this liquid type of bitumen.
The cationic emulsified asphalt is a stable mixture of fine droplets of bitumen dispersed continuously in water by a chemical material called cationic emulsifier.
Compared to other bitumen emulsions, cationic bitumen emulsion is more widely used around the world. It is used for surfacing, cold mix asphalt, and road construction.
Let’s become deeper into this liquid type of bitumen.
Production of Cationic Bitumen Emulsion
To produce cationic bitumen emulsion, we need pure bitumen, water, and a cationic emulsifier.
In general, for the production of cationic emulsion bitumen, it is necessary to dissolve less than 1 %wt of cationic emulsifiers in water.
Then, by using a mill which is equipment for producing the cationic bitumen emulsion, the small drops of hot bitumen are separated and mixed well with the solution of water and cationic emulsifier.
After that, cationic emulsifiers make fine bitumen drops positive.
In addition to the fact that cationic bitumen emulsion is harder to dissolve in water than the anionic type, a series of additives are also needed to make the dissolution process easier.
Cationic Bitumen Emulsion Grades
Cationic bitumen emulsions are classified based on setting time.
An emulsion’s setting time is a measure of how fast dispersed bitumen drops are joined together and settle on the paving surface.
In other words, after applying bitumen emulsion to the surface, the setting time showed how long it takes for bitumen and water to separate from each other.
This classification for cationic emulsion includes:
-Rapid Setting (RS)
This type of bitumen emulsion breaks as soon as it is applied on any surface.
-Medium Setting (MS)
This type of bitumen emulsion is used in road constructions that have medium grain sizes. After applying MS cationic emulsion bitumen on the surface, it will break only if dust and small particles of air enter it. Otherwise, its water should evaporate. Then it can play the role of bitumen and bind the grains.
-Slow Setting (SS)
Bitumen emulsions of this type have a slow setting time. Bitumen setting time in this type only depends on the water evaporation rate.
It is used on aggregates that are very fine.
This type of bitumen can penetrate into very small pores without breaking.
The below table shows different types of cationic bitumen emulsion:
| CRS | CMS | CSS |
| CRS-1 | CMS-1 | CSS-1 |
| CRS-2 | CMS-2 | CSS-2 |
| CRS-1h | CMS-1h | CSS-1h |
| CRS-2h | CMS-2h | CSS-2h |
After each nomination category, numbers 1 and 2 can come to show the higher viscosity. For example viscosity of CSS-1 is lower than CSS-2.
Sometimes to show whether the base bitumen has a hard penetration, the “h” alphabet is used. For example, pure bitumen of CRS-1 has a lower penetration value than CRS1h.
Read more about emulsion bitumen
Cationic Emulsion Bitumen Applications
In general, one of the most important applications of cationic emulsion bitumen is asphalt repairs and cold asphalt production.
Click to get familiar with Road Construction.
Asphalt may be damaged over time due to various factors, such as erosion. This causes the asphalt surface to become slippery.
It is also possible that the bitumen binder has been exposed to oxidation due to the reaction with Oxygen molecules in the air. During this time this oxidation has led to the hardening and brittleness of the asphalt. This type of oxidized asphalt is called aged asphalt.
Accordingly, in the situations mentioned, CRS types can be used in the following ways:
- It is possible that before applying asphalt, a layer of cationic emulsion bitumen is applied to the surface, and then asphalting is done.
- In repairing damaged asphalt, a layer of bitumen emulsion is sprayed on the road surface, which is called chip seal.
- After that, unshaped large aggregates are poured into the emulsion bitumen layer.
- Sometimes these methods are used for preventing erosion or to seal asphalt which is called on-layer asphalt.
- In some cases, emulsion bitumen is used to prepare multi-layered asphalt on old asphalt to repair the road.
The life of these multi-layer asphalts is longer than the single-layer ones, and their cost is lower in comparison to the quality and increased life span they give to the asphalt.
In this type of asphalt, first, coarse-grained stones are poured on the emulsion bitumen which is sprayed on the surface, and then another layer of emulsion bitumen is poured.
Stone grains are then poured onto the surface in large to small sizes.
So the space between larger stones is filled by smaller ones and the wear rate is reduced.
The following can be mentioned from the use of CSS types:
- It can be sprayed on asphalt to prevent abrasion and erosion of asphalt
- Applied as a thin layer before starting asphalting, this coating is called prime coat
- In order to fill cracks on aged asphalt, it can be sprayed onto the surface
- In areas with very fine and worn soil, it is used to cover surfaces to prevent dust from spreading
- It can be used to prepare micro-surfacing for clean cracked and aged asphalt surfaces. In this method, aggregates and emulsion bitumen are mixed by the machine and then applied to the surface.
This type of coverage is applied to highways and areas with heavy traffic.
Different protective asphalts can be used in road construction to maintain the road. In each of them there exist emulsion bitumen. Below, we have mentioned the most common grade of emulsion bitumen that is suitable for each of these protective asphalt.
| CRS-1 | CRS-2 | CMS-2 | CMS-2h | CSS-1 | CSS-1h | |
| Protective asphalt with aggregates | ||||||
| Seal coatOne & multi-layer | * | * | ||||
| Sand seal | * | * | ||||
| Slurry seal | * | * | ||||
| micro-surfacing | * | |||||
| Sandwich seal | * | |||||
| Cape seal | * | |||||
| Bituminous coatings without asphalt | ||||||
| Fog seal | * | * | ||||
| Prime coat | * | * | ||||
| Take coat | * | * | ||||
| Dust settling | * | * | ||||
| Mulching | * | * | ||||
| Filling cracks | * | * | ||||
Let’s explore bitumen emulsion application in details
Unlike anionic emulsions, cationic emulsion bitumen does not dissolve easily in water, and adding additives to them is a challenge.
If the charge of additives to cationic emulsion bitumen is negative, the emulsion will leave the liquid state and its bitumen droplets will stick together.
Due to this property, it is better to apply cationic bitumen emulsion on surfaces where their minerals have a negative charge. Because the negatively charged mineral creates a strong bond with the fine droplets of bitumen that carry the positive charge. Due to this strong interaction, a uniform surface is covered with bitumen.