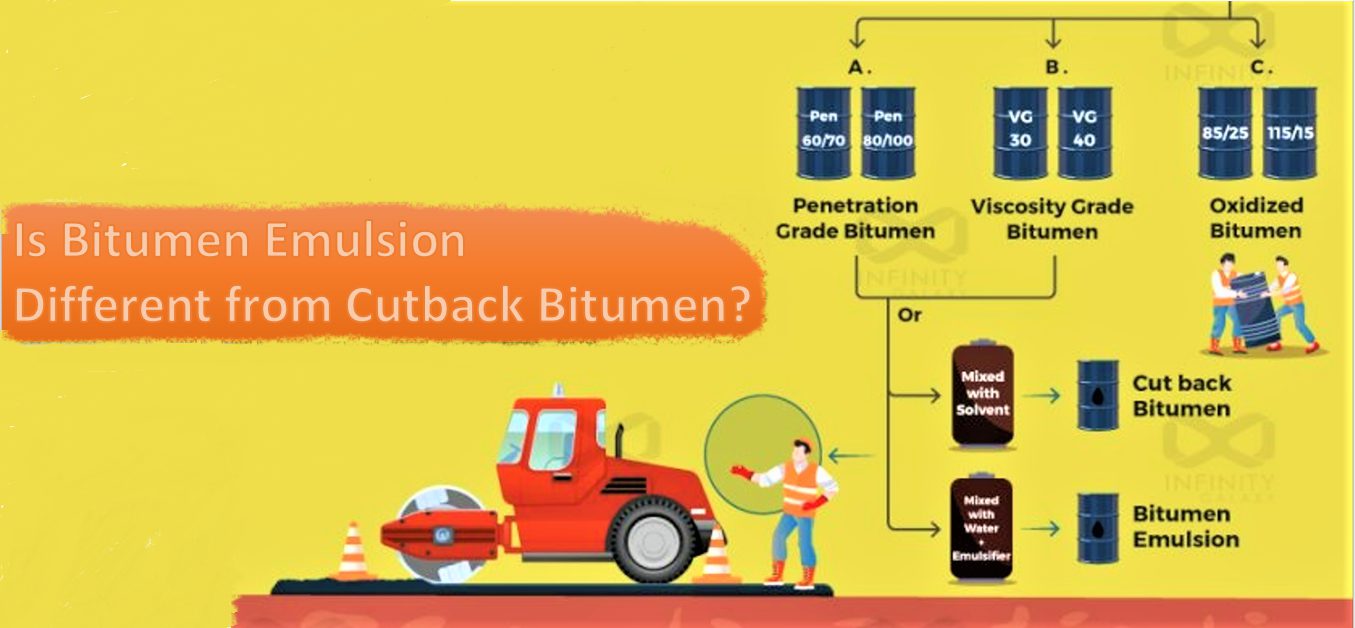
Cutback bitumen is a liquid bitumen obtained by dissolving penetration bitumen in a solvent. The solvents are obtained from the oil distillation process in refineries.
Depending on the drying time or, in other words, the rate of solvent evaporation, cutback bitumen can be classified into three types:
- Slow-Curing (SC)
- Rapid-Curing (RC)
- Medium-Curing (MC)
Note: The solvent evaporation rate is controlled by solvent types.
Also, each mentioned above are categorised into different grades according to the viscosity value or fluidity property in centi-Stocks (cSt) units.
The amount of solvent controls the viscosity of different grades.
Continue reading to learn more about the types of cutback bitumen and their different grades.
Types of Cutback Bitumen Based on Curing Time
Various solvents extracted from crude oil are used to prepare cutback bitumen.
There is 10 to 50% solvent in cutback bitumen, mostly kerosene, gasoline, diesel oil or fuel oil.
Cutback bitumen is classified based on the relative evaporation rate of the solvent compared to acetone, as listed below:
1- Rapid Curing (RC)
Fast-evaporating solvents at ambient temperature are used to make rapid-curing cutback bitumen. This bitumen is called RC for short.
The evaporation rate of the solvents used in this type of bitumen is 0.3 times more than the evaporation rate of acetone.(1)
Rapid curing grades are used in tack coats, chips seals and sand seals.
Read more about cutback bitumen applications.
2- Medium-Curing (MC)
Medium-curing bitumen is prepared by dissolving penetration bitumen in solvents with medium vaporability or volatility.
Generally, the evaporation rate of these solvents is 0.8 to 0.3 times of acetone evaporation rate.
Commonly, medium-curing cutback bitumens are made with kerosene.
MC does not evaporate fast when mixed with aggregates. For this reason, it is used as a binder in cold asphalt.
3- Slow Curing (SC)
Slow curing bitumen is prepared by dissolving penetration bitumen with heavy distillate solvents.
Their evaporation rate is 0.8 times lower than the evaporation rate of acetone.
Typical solvents are gasoline or fuel oil.
SC cutback bitumen is used in dust repression and cold mixed asphalt.
Cutback bitumen grades based on viscosity measurements:
Each cutback bitumen type has different grades based on its viscosity range, which is controlled by solvent amount.
The higher the amount of solvent, the lower the viscosity of cutback bitumen. As a result, each type of cutback bitumen has grades with different fluidity.
Due to the higher amount of solvent, some can flow easily at room temperature. Also, there are grades with higher viscosity or lower amount of solvent that must be heated to flow in order to use.
The viscosity or fluidity of a cutback bitumen is measured at 60 degrees Celsius by ASTM D2170 standard method. Each grade belongs to one viscosity range.
For example, the viscosity value of an MC cutback bitumen is 83 cSt. According to the below table, it is in the range of 70 to 140 cSt. As a result, the cutback bitumen is MC-70.
Read about the ‘Dynamic Viscosity’ test method.
| Cutback Types | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Viscosity Range (sCt) | Rapid Curing | Medium Curing | Slow Curing |
| 30-60 | RC 30 | MC 30 | SC 30 |
| 70-140 | RC 70 | MC 70 | SC 70 |
| 250-500 | RC 250 | MC 250 | SC 250 |
| 800-1600 | RC 800 | MC 800 | SC 800 |
| 3000-6000 | RC 3000 | MC 3000 | SC 3000 |