The difference between bitumen, tar and asphalt is in their origin, applications, price, physical and chemical properties.
Bitumen and tar are closely similar to each other but asphalt is completely a different composition from bitumen and tar.
In the below, you will read the details about each of these factors that shows the differences between bitumen, tar and asphalt.
Difference in Origins
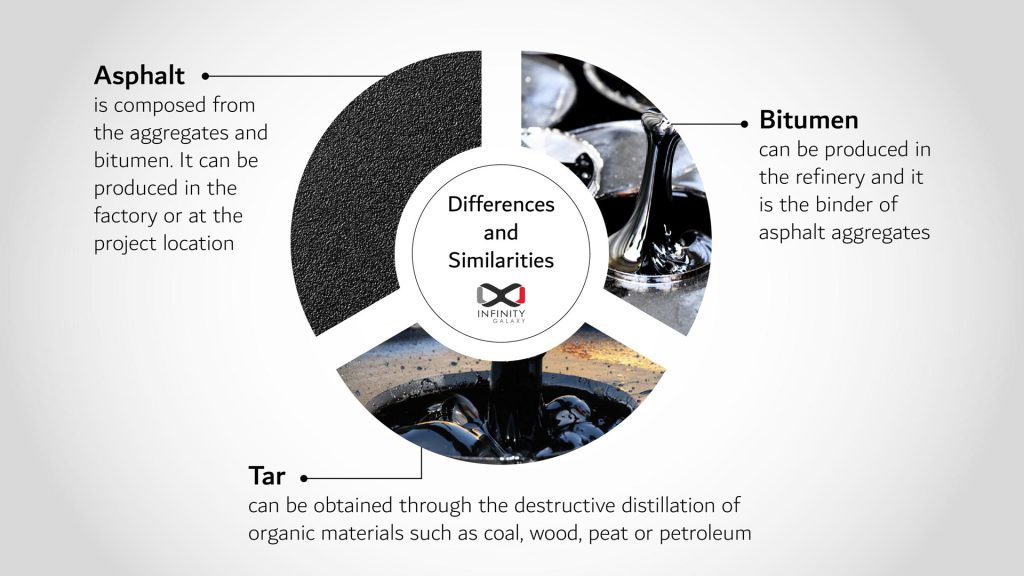
Bitumen
The bitumen has two origins.
It can be produced in the petroleum refinery or it can be extracted from the mines which is gilsonite.
To produce the refinery bitumen, after taking crude oil to an atmospheric distillation tower in a refinery, the oil will be heated to temperatures between 300 and 350 degrees Celsius.
As a result, lighter fractions of crude oil separate from non-boiling components. This process leaves a sticky substance at the bottom of the tower, which we call the vacuum bottom. It is the raw material for producing refinery bitumen.
Tar
Tar can be obtained through the destructive distillation of organic materials such as coal, wood, peat or petroleum.
The process involves heating the organic material in the absence of air which results in obtaining tar.
Asphalt
Asphalt is composed from the aggregates and bitumen. It can be produced in the factory or at the project location.
Differences in Applications
Bitumen
Bitumen has more than 130 applications in different industries. More than 85% of bitumen application is in the road construction but it can also be used in waterproofing, roofing and coating.
You can read the list of bitumen applications in the Bitumen Applications and Uses page.
Tar
Tar also has different applications as below:
- Pavement sealer
- Roofing material
- Wood preservative
- Medicinal applications for eczema and skin treatment
- Industrial applications like making plastics and rubber
Asphalt
Asphalt just can be used on the road surface. It doesn’t have any special application in other industries.
Difference in Price
These three material prices can be determined based on different factors including the market supply and demand, quality and their grades.
But generally, the bitumen price is lower than both tar and asphalt.
Tar has a high price compared to bitumen because usually its supply quantity is less than bitumen.
Sometimes, due to the raw material prices of asphalt, the asphalt price can be more than bitumen and tar.
Differences in Physical Properties
Generally, these three materials have differences in the below physical properties:
- State
- Color
- Density
- Melting Point
- Boiling Point
State
Bitumen state can be in the liquid form with different viscosities or a brittle solid. Tar is a liquid with high viscosity and the asphalt has a solid composition that its viscosity is too high.
Color
The color of bitumen is dark brown or black which indicates it has the components of asphaltene and resins. Tar color is dark black due to the high carbon content.
Asphalt color depends on the aggregates and its binder which is bitumen. Currently, in some countries different types of asphalt with different colors are produced.
Density
The density of bitumen is in the range 1.01-1.05 g/cm³ in the temperature range of 25°C to 85°C.
Tar density in this temperature is higher than bitumen and is in the range 1.15 to 1.4 g/cm³.
The asphalt density is 2.2 to 2.4 g/cm³. The higher the density of the asphalt, the more durable it is.
Boiling Point
The boiling point of tar can range from 100°C to 400°C, depending on its composition and the method of production. Bitumen boiling point is in the range 200°C to 525°C and the asphalt boiling point is typically around 400°C to 500°C.
Melting Point
Generally, these substances don’t have a clear melting point like a solid substance. When they become increasingly viscous as they are heated, they eventually become liquid.
But, the probable melting point of these three material is as below:
- The melting point of bitumen is around 120-150°C
- The melting point of tar is around 42-46°C
- The melting point of asphalt is around 135-165°C

Differences in Chemical Properties
Bitumen, tar and asphalt have differences in the below chemical properties:
- Carbon Content
- Reactivity
- Flammability
- Water resistance
- Acid resistance
- Adhesive power
- Setting time
Carbon Content
The carbon content of bitumen and tar is more than asphalt. Generally, bitumen has lower carbon content in comparison to tar but 80% to 90% of bitumen is carbon.
Bitumen with a higher carbon content may be more viscous and hard, while bitumen with a lower carbon content may be less durable and more susceptible to aging and weathering.
On average, tar contains between 50% to 90% carbon. Asphalt carbon content depends on the type of bitumen that is used to bind the aggregates.
Reactivity
In general, bitumen is a relatively inert material in the ambient temperature and has low reactivity but when it is exposed to certain conditions, such as high temperatures or exposure to oxygen, bitumen can undergo chemical reactions that can cause it to degrade or become more reactive.
Tar is also the same as bitumen that has low reactivity. But sometimes it can react with other chemicals such as oxygen, nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide in the environment. These reactions of tar and chemicals can lead to the formation of secondary pollutants such as acid rain.
Asphalt can react with oxygen, water, and acids which can cause changes in its resistance against the cracking.
Flammability
Generally, according to the flash and fire point test of bitumen, bituminous materials have a high flammability. Their flash point is in the range 200 °C to 300 °C and the fire point is between 250 °C to 350 °C.
Tar is flammable too, it can be ignited by spark and friction. Its flash point is in the range 150 °C to 300 °C while its fire point is 200°C to 400 °C.
Asphalt itself is not flammable but the protective asphalts that are cut back bitumen can be flammable because there exists petroleum based solvent in its composition.
Water Resistance
The water resistance of asphalt and bitumen is high, but tar has less water resistance in comparison to these materials.
Acid Resistance
Compared to bitumen and asphalt, tar is generally more resistant to acids. This is because tar is typically made from coal or wood and contains a higher percentage of aromatic hydrocarbons than either bitumen or asphalt. These hydrocarbons have a greater resistance to chemical degradation, including acid attacks.
Bitumen and asphalt, on the other hand, are both derived from petroleum and contain fewer aromatic hydrocarbons than tar. As a result, they are generally less resistant to acid attacks than tar. However, the exact level of acid resistance can vary depending on the specific type and quality of the material used.
Adhesive Power
One of the main reasons that bitumen and tar are used in waterproofing, insulation and sealing is their adhesive power. The asphalt itself has no adhesive power but the bitumen and tar have a strong adhesion. Bitumen adhesion is less than tar and tar adhesion is too high.
Setting Time
In comparison to bitumen and asphalt, the setting time of tar is high.
Generally the setting time of bitumen depends on its grades, temperature and wind. For example, the setting time of bitumen emulsion CRS-1 is higher than the CMS-1.
Asphalt setting time is too low and it takes time for asphalt to be set on the surface.
What is the difference between asphalt vs bitumen?
Asphalt is a mixture of bitumen and aggregates, whereas bitumen is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or brittle solid. But, in some American and European countries, both bitumen and asphalt have the same meaning as a black, viscous liquid or brittle solid.
Asphalt and bitumen are commonly used in road construction; however, bitumen has numerous other applications. Asphalt is the final layer on road surfaces, and bitumen is the binding agent that holds the asphalt together.
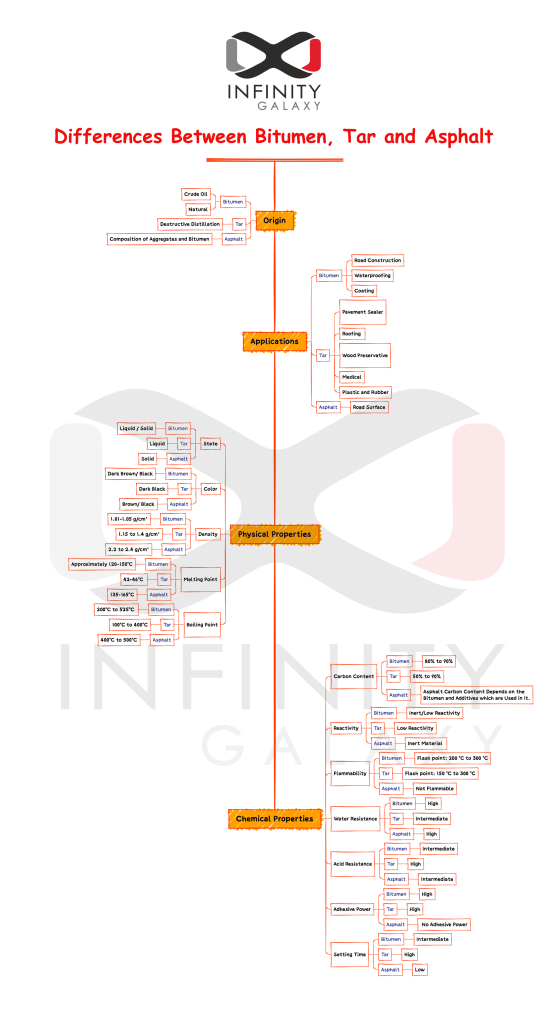
In the following infographic, we summarized the key differences between bitumen, tar, and asphalt. To see it in higher resolution, click here.





4 comments
Steve Goldthorpe
Do the properties of bitumen that is used to make asphalt change in storage? Is fresh bitumen better for road making than aged bitumen?
Tahir M.Ali
Peace to you What is commonly used in road construction, tar or bitumen? Are both used for common puposes ore are they distinct in their functions? Sorry for the unprofessional question? I am not into it liked th business related to it.