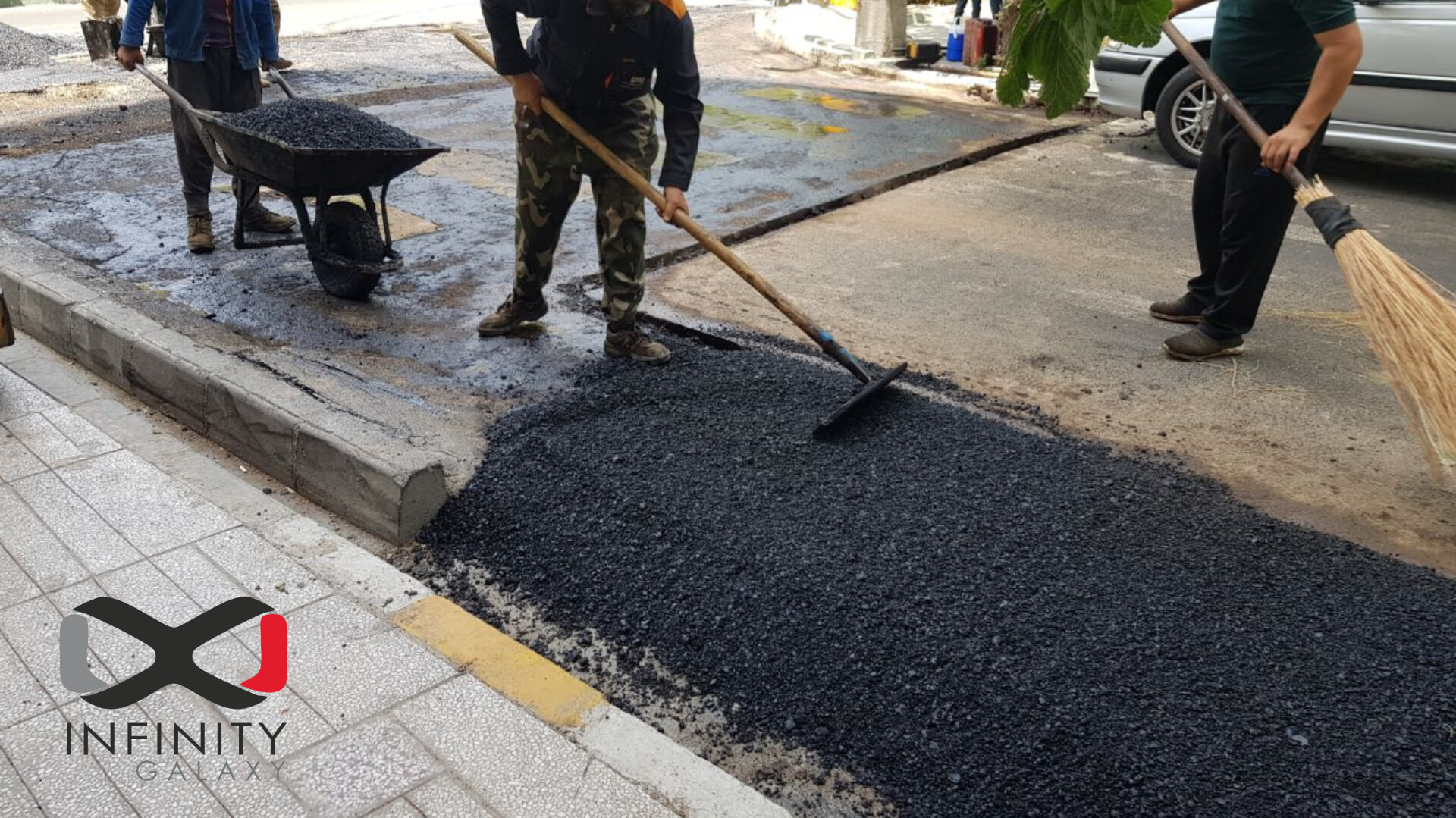
A flexible pavement consists of main layers and sub layers. Different pure bitumen and liquid bitumen can be used in these layers.
The main layers are surface course, base course and sub base course. The sub layers that are placed between the main layers to stick them together are tack coat, binder course and prime coat. In addition, protective asphalts are used to protect the surface course from damages.In this article, we will explain about the types of bitumen that are used in each layer. Also, you can take a look at the below info-graphic to understand which types and grades of bitumen can be used in the layers of flexible pavement.
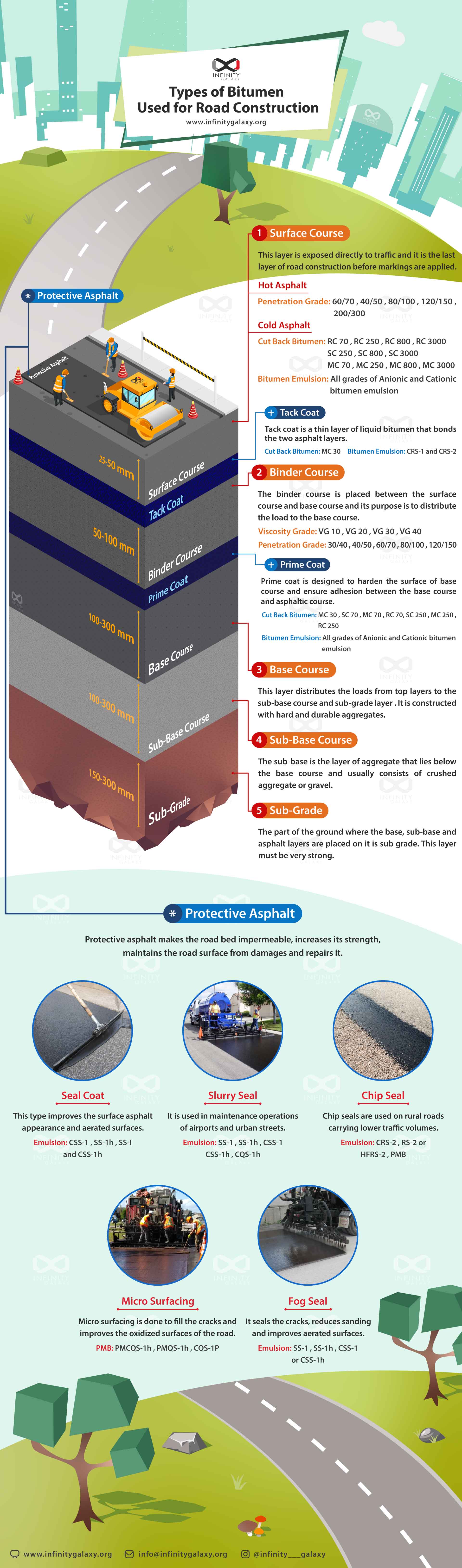
Tack Coat
When we have two layers of asphalt and we want to bond these two layers together, we use a thin layer of liquid bitumen. This layer is a tack coat layer.
Tack coat presence is essential for bonding asphalt layers.
| Different Types of Bitumen in Tack Coat | |
|---|---|
| Cut Back | Emulsion |
| MC 30 | CRS-1, CRS-2 |
Binder Course
Binder course is placed between the surface course and base course.
It prevents the surface course from moving and shifting.
Binder Course’s hot asphalt consists of coarse aggregates and bitumen.
Binder course asphalt is not suitable for road and street surfaces due to coarse aggregates. Its bitumen content is less than the bitumen in surface course asphalt.
This layer should be covered with the surface course that has much finer aggregates in its asphalts.
Different grades of pure bitumen can be used in the hot asphalt of binder course. In the table below, we clarify these grades for you:
| Different Types of Bitumen in Binder Course Hot Asphalt | |
|---|---|
| Penetration Grade | Viscosity Grade |
| 30/40 | VG 10 |
| 40/50 | VG 20 |
| 60/70 | VG 30 |
| 80/100 | VG 40 |
| 120/150 | |
Prime Coat
The surface of the base course is sandy. It is better to pour a thin layer of liquid bitumen on this surface before asphalting it. This thin layer of liquid bitumen is called a prime coat.
Applying prime coat has several advantages:
- It seals the surface of base course
- It penetrates into the pores of the base course. This causes that asphalt adheres better to the base course
| Different Types of Bitumen in Prime Coat | |
|---|---|
| Cut Back | Emulsion |
| SC 70, SC 250 | All Grades of Cationic and Anionic Emulsion Bitumen |
| RC 70, RC 250 | |
| MC 30, MC 70, MC 250 | |
Base Course
The base course is placed below the asphalt layers and on the sub base course.
It can be composed of mountain gravel, riverbed rocks or macadam.
Macadam is a combination of coarse aggregates and fine particles of stone.
The base layer has a higher permeability than the sub base course.
This layer transfers the pressure and tensions applied to it from the upper layers to its lower layer which is sub base course.
Sub Base Course
The sub base course is usually the first layer that is placed on the prepared bed pavement.
It usually consists of riverbed aggregates, rocks extracted from mines and alluvial fans.
We can stabilize the sub base soil with materials such as bitumen, cement and chemicals.
The materials we use for the sub base layer must have good granulation.
If granulation is appropriate, fine particles from the sub grade layer cannot penetrate into the sub base layer.
Sub Grade
Sub grade is the part of the ground where the base course, sub-base course and asphalt layers are placed on it. This layer must be very strong.
The sub grade must be able to tolerate the loads transferred from the pavement.
A sub grade that can withstand loads for a long time without deforming or breaking is known as a good sub grade.
Protective Asphalt
Protective asphalts are usually used as a temporary coating in the road construction industry. It is not the main component of the road.
These layers are mostly used to make the asphalt impermeable and prevent erosion of the surface course.
After 3 to 5 years, the hot asphalt must be implemented on protective asphalts. Because after this period, the life of protective asphalt expires and the main layer of asphalt may be damaged over time.
The main advantage of protective asphalts is their low price. Because, the main component in these asphalts is liquid bitumen, which has a lower price than other types of bitumen.
Different Types of Protective Asphalts
There exist several types of protective asphalts including:
- Seal Coat
- Slurry Seal
- Chip Seal
- Micro Surfacing
- Fog Seal
In each of these protective asphalts, different grades of Cut back bitumen and Emulsion bitumen is used.
Seal Coat
Seal coat is a type of low-thickness protective asphalt that is used to improve the durability of road, prevent the surface from failure and make it water-resistance.
Different types of emulsion bitumen can be used in seal coating including CSS-1, SS-1h, SS-l, and CSS-1 h.
Slurry Seal
Slurry sealing is used in the maintenance of asphalt pavements, reducing the amount of damage caused by bitumen oxidation.
The suitable bitumen for this type of road maintenance is bitumen emulsion and cutbacks. SS-1, SS-h1, CSS-1, CSS-1h, CQS-1h are suitable for slurry sealing.
Chip Seal
The main reason for using a chip seal on an asphalt surface is to protect the pavement from the damaging effects of the weather, such as the sun’s heat and humidity.
The suitable bitumen for chip sealing is rapid setting emulsion including a CRS-2, RS-2, HFRS-2 and PMB.
Micro Surfacing
In micro surfacing protective asphalt, we can use polymer modified bitumen emulsion. In this type of asphalt, we use SBS or poly bitex which are new additives for bitumen.
Fog Seal
Fog seal is a coating of asphalt emulsion that protects the streets and road surfaces from oxidation.
This type of protective asphalt increases the durability of pavements by adhering to the road surface as it dries and leaving a tough film.
How Much Bitumen is Used in Road Construction?
The quantity of bitumen used in the road surface depends on the width of the road and the thickness of the asphalt.
But in general, the quantity of bitumen per square meter is about 7 kg for an asphalt with a thickness of 6 cm.
FAQ
Why is bitumen used in road construction ?
Bitumen is a strong adhesive that can play a role as a glue to bind all the hard aggregates to each other. This material has a high waterproofing property and can be good resistant to water and humidity.
How many layers are in the bitumen road?
There are 7 layers in the bitumen road including surface course, tack coat, binder course, prime coat, base course, sub base course and sub grade.
What is the CRS-1h, and when we can use it?
CRS-1h is a cationic bitumen emulsion composed of water and harder grades of penetration bitumen. The rapid separation of bitumen and oil in CRS-1h makes it ideal for coating and sealing in road construction, such as chip seal, sand seal, and surface repairs.
Infinity Galaxy, Bitumen Supplier for Road Construction Projects
In this paper, we had a brief description of different grades of bitumen that can be used in road construction.
Infinity Galaxy, as a reliable bitumen supplier based on middle east, provides these bitumen grades.
If you are looking for these grades of bitumen, keep in touch with our sales experts by filling out below form.
"*" indicates required fields







