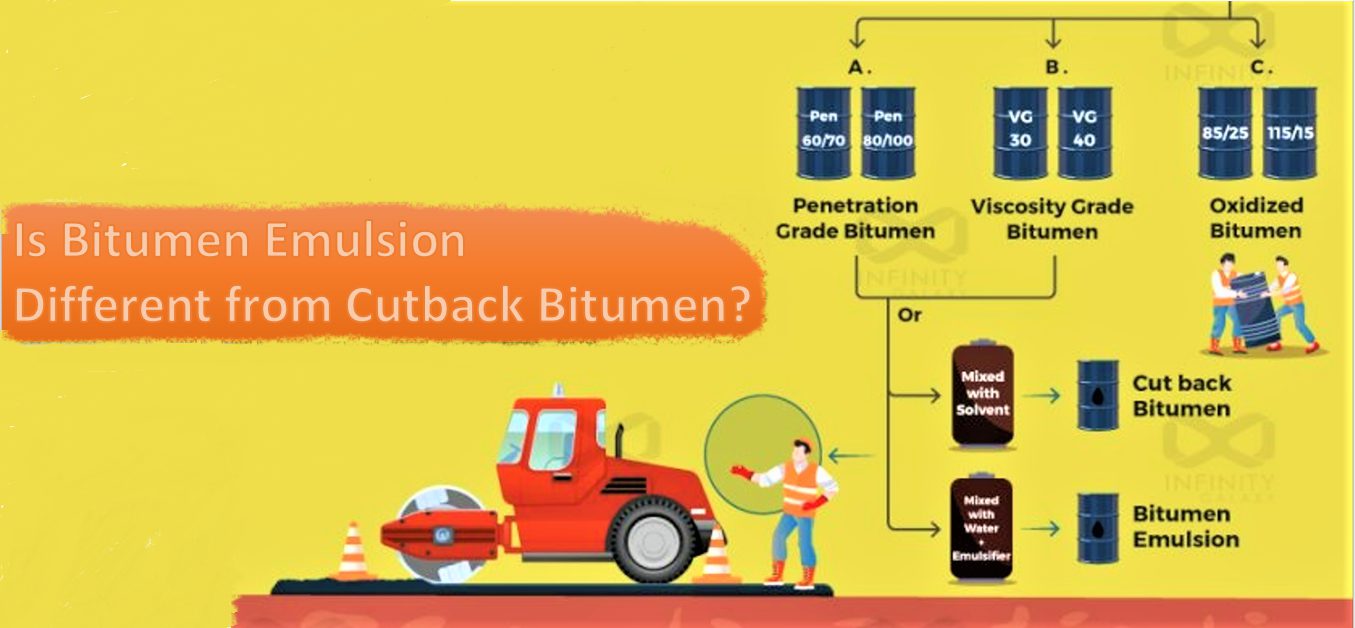
Cutback bitumen is produced by dissolving penetration bitumen with petroleum based solvents.
The production steps of cutback bitumen include the following:
- Preparation of bitumen and solvent
- Mixing bitumen and solvent with the help of a suitable stirrer or pump
The above steps must be done under expert supervision and in safe conditions. Also, the amount of the desired material should be carefully selected. Because it is effective in cutback bitumen performance. In addition, petroleum solvents are costly, so their consumption should be optimal.
In preparing cutback bitumen, it is important to use tools that prevent solvent vapors from escaping.
The obtained cutback bitumen should have characteristics that comply with international standards. These standards include:
- ASTM D2026
- D2027 D2028
- AASHTO M82-75 (2008)
- ASTM D2028 or AASHTO M92-92 (2008)
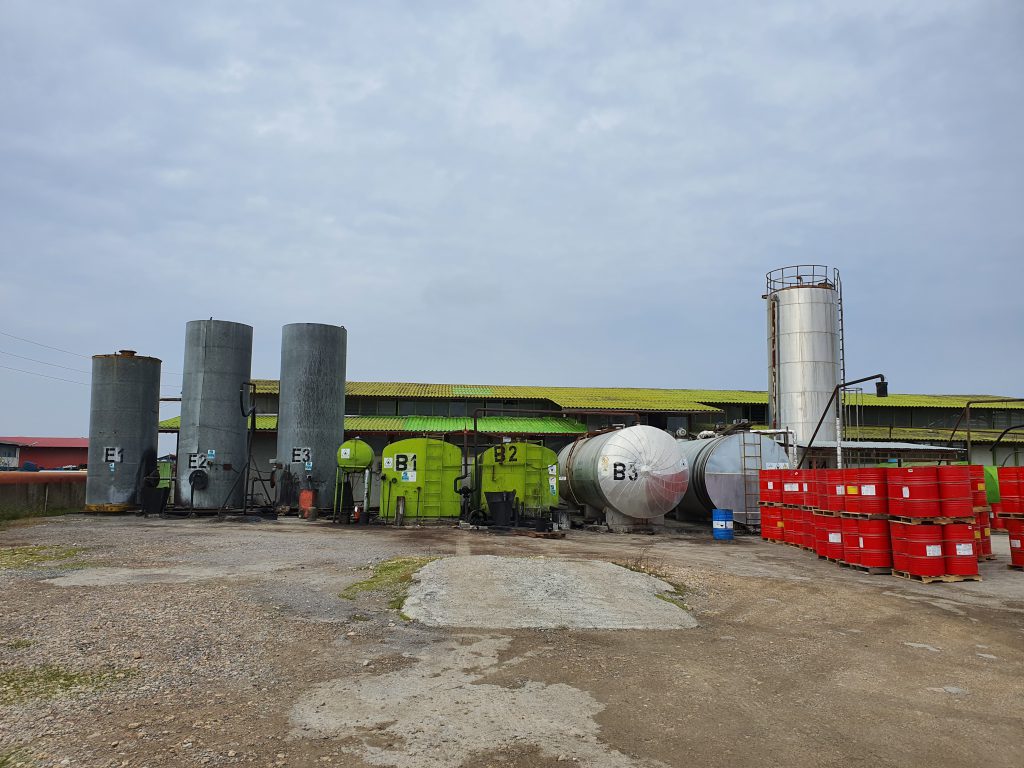
1- Preparing Cut back Bitumen Ingredients
In the first step, the solvent and bitumen must be prepared.
An expert should determine the required solvent and its amount. In addition, the application and environmental conditions are also practical.
Click to read about Cutback Bitumen Uses
Solvent
Solvent makes up 10 to 50% of the total volume of cutback bitumen. The solvent used in cutback bitumen are:
- Rapid curing (RC) contains petrol/gasoline
- Medium curing (MC) contains kerosene
- Slow curing (SC) contains diesel oil
The purpose of using a solvent is to reduce the viscosity of bitumen and helps it to penetrate into fine cracks.
A specific solvent is used depending on the application and the region’s climatic conditions. In some cases, to reach the cutback bitumen adapted to weather conditions, it is necessary to mix two solvents to prepare cutback bitumen.
Bitumen
Different types of penetration grade bitumen to produce cutback bitumen are 70/100, 160/220 and 250/330.
If the bitumen viscosity is high, it needs to be preheated for better transferring and mixing with the solvent.
2- Mixing Bitumen and Solvent
After the bitumen and solvent are prepared, they are transferred to the mixing unit by pumps.
The solvent amount usually is lower than the bitumen amount. Therefore, it is better to transfer the solvent into the production unit at a lower speed than bitumen. As a result, the two materials are well mixed.
In some factories, a colloidal mill is used for mixing materials. This mill converts bitumen into smaller droplets to dissolve more uniformly and faster in the solution.
After mixing the materials, the final product, which is cutback bitumen, is cooled by a compressor.
Finally, the cutback is terminated from the production system to the storage tank or transferred for packing.
If you have any questions and inquiries, contact us via the comment section or WhatsApp.