What is PG Bitumen?
Bitumen Performance Grade or PG is a type of bitumen which is graded according to its performance in different temperatures.
This bitumen is produced based on the AASHTO M 320-10 and ASTM D6373 − 1.
Read more details about PG bitumen below.
Introduction of Bitumen Performance Grade
Generally, the bitumen is classified based on the penetration degree which shows its hardness and viscosity degree which shows the consistency.
The bitumen penetration degree is measured in 25 degree celsius and its viscosity is obtained in both 60 and 135 degree celsius.
After some years the SHRP engineers understood that one of the most important parameters about bitumen is temperature. They realized that in the bitumen classification, the temperature has been ignored while the performance of the bitumen depends mainly on the temperature.
PG Bitumen Grading System
PG bitumen grading system is based on the bitumen performance in low, medium and high temperatures.
For example, the PG 58-28 means this grade can be used in an area where its maximum temperature is 58 and its lowest temperature is -28 degree celsius.
It means that this bitumen can not perform well in the temperatures higher than 58 degree celsius and it can not tolerate the temperature below -28 degree celsius.
The positive number which is 58 shows the average temperature of the seven successive days of the highest pavement temperature in the summer season. The negative number which is -28 indicates the lowest temperature of the pavement in the seven successive days of the winter season in degrees Celsius.
In the below, we have a table of different grades of PG bitumen.
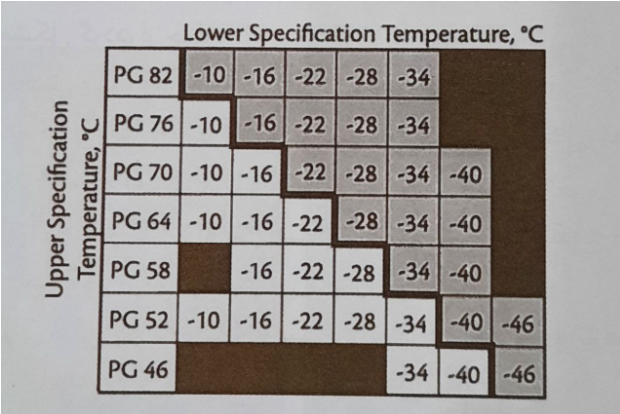
PG grades are mainly divided into Modified and Unmodified bitumen types. To distinguish the modified PG bitumen from unmodified PG bitumen, we add both low and high temperature of the PG bitumen together.
If the sum is greater than 92, the PG bitumen is a polymer modified bitumen. As an example, a PG 76-22 is considered as a polymer-modified binder since the sum is 98. Another example, a PG 64-10 is an unmodified binder while the sum of 64 and 10 is equal to 74.
Generally, the grades in the dark part of the table are considered to be modified bitumen.
When the difference between the high temperature and the low temperature is more than 92 degrees Celsius, it is necessary to use a modifier and it increases the price of bitumen.
PG Bitumen Tests
The PG bitumen is tested based on the different methods of the AASHTO standard. For PG bitumen, 3 parameters which are related to rutting, fatigue and thermal cracking should be tested.
For PG bitumen, besides the solubility test, flash point test, specific gravity and softening point tests, there are new test methods including:
- Viscosity Determination of Bitumen Using Rotational Viscometer (RV)- AASHTO T 316
- Determining the Rheological Properties of Bitumen Using a Dynamic Shear Rheometer (DSR)-AASHTO T 315
- Determining the Fracture Properties of Bitumen in Direct Tension (DT) – AASHTO T314
- Determining the Flexural Creep Stiffness of Bitumen Using the Bending Beam Rheometer (BBR)-AASHTO T 313
- Test for Effect of Heat and Air on a Moving Film of Bitumen (Rolling Thin-Film Oven Test)-AASHTO T 240
- Accelerated Aging of Bitumen Using a Pressurized Aging Vessel (PAV)-AASHTO R 28
- Elastic Recovery Test- AASHTO T301
- Determining the Separation Tendency of Polymer from Polymer -Modified Bitumen – ASTM D7173
PG Bitumen Specifications
Infinity Galaxy supplies the below bitumen PG grades:
| Bitumen PG 70-16 Specification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Specification | Unit | Value | Method |
| Average 7-Day Maximum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | < 70 | – |
| Minimum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | > -16 | – |
| Flash Point Temperature | °C | Min230 | AASHTO T48 |
| Viscosity Maximum 3 Pa.s, Test Temperature | °C | 135 | AASHTO T316 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Minimum 1 KPa Test Temperature | °C | 70 | AASHTO T315 |
| Rolling Thin Film Oven Test (AASHTO T240) | |||
| Mass Change | % | Max1.00 | – |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Minimum 2.2 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 70 | AASHTO T315 |
| Pressure Aging Vessel (PAV) Test (AASHTO R28) | |||
| PAV Aging Temperature | °C | 100 (110) | AASHTO R28 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Maximum 5000 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 31 | AASHTO T315 |
| Creep Stiffiness S Maximum 300 Mpa M-Value Minimum 0.300 Test Temp,@60s | °C | -6 | AASHTO T313 |
| Direct Tension Failure Strain Minimum 1 % Test Temp@1mm/min, | °C | -6 | AASHTO T314 |
| Critical Low Cracking Temperature Critical Cracking Determined by PP42 Test Temp | – | -6 | AASHTO PP42 |
| Bitumen PG 76-10 Specification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Specification | Unit | Value | Method |
| Average 7-Day Maximum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | <76 | – |
| Minimum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | > -10 | – |
| Flash Point Temperature | °C | Min230 | AASHTO T48 |
| Viscosity, T 316, Maximum 3 Pas, Test Temp, °C | °C | 135 | AASHTO T316 |
| Dynamic Shear, T 315, G*/sin Minimum 1.00 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s,°C | °C | 76 | AASHTO T315 |
| Rolling Thin Film Oven Test (T 240) | |||
| Mass Change, Maximum, Percent | % | 1.00 | AASHTO T240 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Minimum 2.2 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 76 | AASHTO T315 |
| Pressure Aging Vessel (PAV) Test (AASHTO R28) | |||
| PAV Aging Temperature | °C | 100 | AASHTO R28 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Maximum 5000 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 37 | AASHTO T315 |
| Creep Stuffiness S Maximum 300 Mpa M-Value Minimum 0.300 Test Temp,@60s | °C | 0 | AASHTO T313 |
| Direct Tension, T 314, Failure Strain, Minimum 0.300 Test Temperature, @60s, °C | °C | 0 | AASHTO T314 |
| Critical Low Cracking Temp, PP42, Critical Cracking Temp Determined by PP 42,Test Temp, °C | – | 0 | AASHTO PP42 |
| Bitumen PG 58-16 Specification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Specification | Unit | Value | Method |
| Average 7-Day Maximum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | <58 | – |
| Minimum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | > -16 | – |
| Flash Point Temperature | °C | Min230 | AASHTO T48 |
| Viscosity Maximum 3 Pa.s, Test Temperature | °C | 135 | AASHTO T316 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Minimum 2.2 KPa Test Temperature | °C | 58 | AASHTO T315 |
| Rolling Thin Film Oven Test (T 240) | |||
| Mass Change, Maximum, Percent | % | Max1.00 | AASHTO T240 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Minimum 2.2 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 58 | AASHTO T315 |
| Pressure Aging Vessel (PAV) Test (AASHTO R28) | |||
| PAV Aging Temperature | °C | 100 | AASHTO R28 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Maximum 5000 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 25 | AASHTO T315 |
| Creep Stuffiness S Maximum 300 Mpa M-Value Minimum 0.300 Test Temp,@60s | °C | -6 | AASHTO T313 |
| Direct Tension Failure Strain Minimum 1 % Test Temp@1mm/min, | °C | -6 | AASHTO T314 |
| Critical Low Cracking Temperature Critical Cracking Determined by PP42 Test Temp | – | -6 | AASHTO PP42 |
| Bitumen PG 70-10 Specification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Specification | Unit | Value | Method |
| Average 7-Day Maximum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | 70 | – |
| Minimum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | > -10 | – |
| Flash Point Temperature | °C | Min230 | AASHTO T48 |
| Viscosity Maximum 3 Pa.s, Test Temperature | °C | 135 | AASHTO T316 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Minimum 2.2 KPa Test Temperature | °C | 70 | AASHTO T315 |
| Rolling Thin Film Oven Test (T 240) | |||
| Mass Change | % | Max1.00 | AASHTO T240 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Minimum 2.2 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 70 | AASHTO T315 |
| Pressure Aging Vessel (PAV) Test (AASHTO R28) | |||
| PAV Aging Temperature | °C | 100 | AASHTO R28 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Maximum 5000 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 34 | AASHTO T315 |
| Creep Stuffiness S Maximum 300 Mpa M-Value Minimum 0.300 Test Temp,@60s | °C | 0 | AASHTO T313 |
| Direct Tension Failure Strain Minimum 1 % Test Temp@1mm/min, | °C | 0 | AASHTO T314 |
| Critical Low Cracking Temperature Critical Cracking Determined by PP42 Test Temp | – | 0 | AASHTO PP42 |
| Bitumen PG 82-10 Specification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Specification | Unit | Value | Method |
| Average 7-Day Maximum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | 82 | – |
| Minimum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | > -10 | – |
| Flash Point Temperature | °C | Min230 | AASHTO T48 |
| Viscosity Maximum 3 Pa.s, Test Temperature | °C | 135 | AASHTO T316 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Minimum 2.2 KPa Test Temperature | °C | 82 | AASHTO T315 |
| Rolling Thin Film Oven Test (T 240) | |||
| Mass Change | % | Max1.00 | AASHTO T240 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Minimum 2.2 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 82 | AASHTO T315 |
| Pressure Aging Vessel (PAV) Test (AASHTO R28) | |||
| PAV Aging Temperature | °C | 100 | AASHTO R28 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Maximum 5000 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 40 | AASHTO T315 |
| Creep Stuffiness S Maximum 300 Mpa M-Value Minimum 0.300 Test Temp,@60s | °C | 0 | AASHTO T313 |
| Direct Tension Failure Strain Minimum 1 % Test Temp@1mm/min, | °C | 0 | AASHTO T314 |
| Critical Low Cracking Temperature Critical Cracking Determined by PP42 Test Temp | – | 0 | AASHTO PP42 |
| Bitumen PG 64-22 Specification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Specification | Unit | Value | Method |
| Average 7-Day Maximum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | 64 | – |
| Minimum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | > -22 | – |
| Flash Point Temperature | °C | Min230 | AASHTO T48 |
| Viscosity Maximum 3 Pa.s, Test Temperature | °C | 135 | AASHTO T316 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Minimum 2.2 KPa Test Temperature | °C | 64 | AASHTO T315 |
| Rolling Thin Film Oven Test (T 240) | |||
| Mass Change | % | Max1.00 | AASHTO T240 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Minimum 2.2 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 64 | AASHTO T315 |
| Pressure Aging Vessel (PAV) Test (AASHTO R28) | |||
| PAV Aging Temperature | °C | 100 | AASHTO R28 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Maximum 5000 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 46 | AASHTO T315 |
| Creep Stuffiness S Maximum 300 Mpa M-Value Minimum 0.300 Test Temp,@60s | °C | -24 | AASHTO T313 |
| Direct Tension Failure Strain Minimum 1 % Test Temp@1mm/min, | °C | -24 | AASHTO T314 |
| Critical Low Cracking Temperature Critical Cracking Determined by PP42 Test Temp | – | -24 | AASHTO PP42 |
| Bitumen PG 46-22 Specification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Specification | Unit | Value | Method |
| Average 7-Day Maximum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | 46 | – |
| Minimum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | > -22 | – |
| Flash Point Temperature | °C | Min230 | AASHTO T48 |
| Viscosity Maximum 3 Pa.s, Test Temperature | °C | 135 | AASHTO T316 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Minimum 2.2 KPa Test Temperature | °C | 46 | AASHTO T315 |
| Rolling Thin Film Oven Test (T 240) | |||
| Mass Change | % | Max1.00 | AASHTO T240 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Minimum 2.2 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 46 | AASHTO T315 |
| Pressure Aging Vessel (PAV) Test (AASHTO R28) | |||
| PAV Aging Temperature | °C | 100 | AASHTO R28 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Maximum 5000 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 46 | AASHTO T315 |
| Creep Stuffiness S Maximum 300 Mpa M-Value Minimum 0.300 Test Temp,@60s | °C | -24 | AASHTO T313 |
| Direct Tension Failure Strain Minimum 1 % Test Temp@1mm/min, | °C | -24 | AASHTO T314 |
| Critical Low Cracking Temperature Critical Cracking Determined by PP42 Test Temp | – | -24 | AASHTO PP42 |
| Bitumen PG 52-28 Specification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Specification | Unit | Value | Method |
| Average 7-Day Maximum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | 52 | – |
| Minimum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | > -28 | – |
| Flash Point Temperature | °C | Min230 | AASHTO T48 |
| Viscosity Maximum 3 Pa.s, Test Temperature | °C | 135 | AASHTO T316 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Minimum 2.2 KPa Test Temperature | °C | 52 | AASHTO T315 |
| Rolling Thin Film Oven Test (T 240) | |||
| Mass Change | % | Max1.00 | AASHTO T240 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Minimum 2.2 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 52 | AASHTO T315 |
| Pressure Aging Vessel (PAV) Test (AASHTO R28) | |||
| PAV Aging Temperature | °C | 100 | AASHTO R28 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Maximum 5000 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 46 | AASHTO T315 |
| Creep Stuffiness S Maximum 300 Mpa M-Value Minimum 0.300 Test Temp,@60s | °C | -24 | AASHTO T313 |
| Direct Tension Failure Strain Minimum 1 % Test Temp@1mm/min, | °C | -24 | AASHTO T314 |
| Critical Low Cracking Temperature Critical Cracking Determined by PP42 Test Temp | – | -24 | AASHTO PP42 |
| Bitumen PG 76-22 Specification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Specification | Unit | Value | Method |
| Average 7-Day Maximum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | <76 | – |
| Minimum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | > -22 | – |
| Flash Point Temperature | °C | >230 | AASHTO T48 |
| Viscosity, T 316, Maximum 3 Pas, Test Temp, °C | °C | 135 | AASHTO T316 |
| Dynamic Shear, T 315, G*/sin Minimum 1.00 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s,°C | °C | 76 | AASHTO T315 |
| Rolling Thin Film Oven Test (T 240) | |||
| Mass Change, Maximum, Percent | % | 1.00 | AASHTO T240 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Minimum 2.2 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | >2.2 | AASHTO T315 |
| Pressure Aging Vessel (PAV) Test (AASHTO R28) | |||
| Dynamic Shear, T 315, G*/sin, Maximum 5000 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 31 | AASHTO T315 |
| Creep Stuffiness, T 313, S, Maximum 300 Mpa, m-value, minimum 0.300 Test Temperature, @60s, °C |
°C | -12 | AASHTO T313 |
| Direct Tension, T 314, Failure Strain, Minimum 0.300 Test Temperature, @60s, °C | °C | -12 | AASHTO T 240 |
| Critical Low Cracking Temp, PP42, Critical Cracking Temp Determined by PP 42,Test Temp, °C | °C | -12 | ASTM D8225 |
| Bitumen PG 76-16 Specification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Specification | Unit | Value | Method |
| Average 7-Day Maximum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | <76 | – |
| Minimum Pavement Design Temperature | °C | > -16 | – |
| Flash Point Temperature | °C | Min230 | AASHTO T48 |
| Viscosity, T 316, Maximum 3 Pas, Test Temp, °C | °C | 135 | AASHTO T316 |
| Dynamic Shear, T 315, G*/sin Minimum 1.00 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s,°C | °C | 76 | AASHTO T315 |
| Rolling Thin Film Oven Test (T 240) | |||
| Mass Change, Maximum, Percent | % | 1.00 | AASHTO T240 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Minimum 2.2 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 76 | AASHTO T315 |
| Pressure Aging Vessel (PAV) Test (AASHTO R28) | |||
| PAV Aging Temperature | °C | 100 | AASHTO R28 |
| Dynamic Shear G*/sin Maximum 5000 KPa Test Temperature, @10 rad/s | °C | 34 | AASHTO T315 |
| Creep Stuffiness S Maximum 300 Mpa M-Value Minimum 0.300 Test Temp,@60s | °C | -6 | AASHTO T313 |
| Direct Tension, T 314, Failure Strain, Minimum 0.300 Test Temperature, @60s, °C | °C | -6 | AASHTO T314 |
| Critical Low Cracking Temp, PP42, Critical Cracking Temp Determined by PP 42,Test Temp, °C | – | -6 | AASHTO PP42 |
PG Bitumen Applications
Performance grade bitumen is highly used in the flexible pavement. Using this type of bitumen can lower the rutting, thermal cracking, Fatigue or alligator cracking, bleeding, block cracking, corrugation and shoving, depression, joint reflection and longitudinal cracking.
Since the rutting and thermal cracking are two main road damages, the suitable PG bitumen grades to use in the flexible pavement to maintain the surface are as below:
PG grades for preventing the thermal cracking are:
- PG 58-34
- PG 64-22
- PG 64-28
- PG 76-22
PG grades which are resistant to rutting are:
- PG 70-22
- PG 70-28
- PG 76-28
- PG 82-22
Below video explains one of the interesting PG bitumen’s benefit:
The Difference between PG Grading and VG Grading System
The viscosity grading system is based on bitumen viscosity at 60 degree Celsius.
Viscosity grading is related to the consistency of the bitumen at a specific temperature. It is not directly related to bitumen performance throughout the anticipated life of the pavement.
But, the PG System measures the fundamental properties like stresses and strains of the bitumen at the various temperature conditions throughout the expected life of the pavement.








