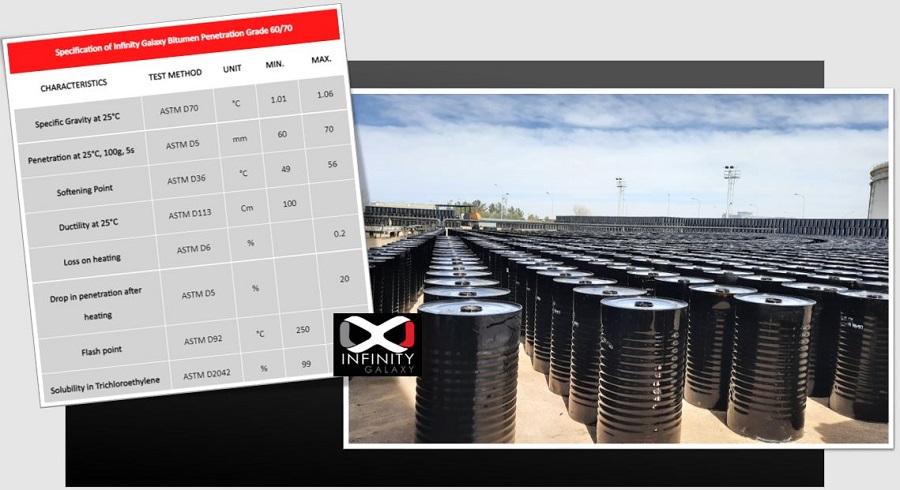
Grading bitumen based on physical properties is essential to get the best performance for construction and other uses. The penetration grading system was developed in the early twentieth century. Bitumen penetration grade is classified using its penetration property. Penetration property is obtained using penetration tests.
What is Penetration Test?
The penetration test measures the consistency and stability of pure bitumen, oxidized bitumen (blown bitumen), and the residue of emulsion bitumen. Penetration tests cannot be carried out for very soft materials with low viscosity, such as tars.
This test classifies bitumen according to its hardness. To classify oxidized bitumen, a softening point test is used in addition to the penetration test.
Penetration value is measured by applying the needle with a load of 100 grams that vertically penetrates into the bitumen for 5 seconds at 25 degrees celsius. The amount of needle movement is the penetration value which is measured in tenths of a millimeter. The higher the penetration of the needle in the bitumen, the higher the bitumen grade.
Watch the video below to see how the test is conducted.
Why do We Use Bitumen Penetration Test?
We use this test to classify bitumen based on penetration value. This helps to choose the proper bitumen in the desired weather conditions for safe road construction.
The soft bitumen (higher penetration) is used in cold weather to avoid cracking. In hot weather, the hard bitumen (lower penetration) is used since it doesn’t get soft due to the heat.
A Review of 11 Important Tests of Bitumen
Different Penetration Grades and Their Applications
The standard penetration value of bitumen is measured from 10 to 450 but the most commonly used range for road is 25 to 200.
Following is a table describing the properties and applications of different penetration grade bitumens:
| Penetration Grade Bitumen; Properties & Applications | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration value (deci-mm) | Softening point (°C) | Application | |
| 40-50 | 52-60 | Tropical areas Mean T > 24° C | |
| 60-70 | 49-56 | Mild climate region 7° C < Mean T < 24° C | |
| 85-100 | 45-52 | Cold climate Mean T < 7° C | |
| 100-120 | 42-49 | Used for road repairs in cold regions | |
Bitumen Penetration Grade Standards
The standard methods used for penetration test of bitumen are:
- ASTM D5
- ASTM D946 & AASHTO M 20 (Penetration @ 25 °C)
- EN 12591 (Penetration @ 25 °C)→NF EN; BS EN; DIN EN; etc.
- EN 1426
- DIN 52210
- SABS 307(Penetration @ 25 °C; Viscosity @ 60 °C after RTFOT)
- IP 49 50 & 167
- EN 1426
Also, the penetration test of bitumen can be done based on the IS Code 1203.
The Apparatus, Components and Test Steps of the Penetration Test of Bitumen
1- Components for the Penetration Test
- Water bath: it contains at least 10 liters of water at a temperature of 25 °C. The sample is immersed in a depth with more than 100 mm from the top. Moreover, the supported perforated shelf, which is the sample placed on it, should be above 50mm from the bottom of the bath.
- Sample container: a small cylindrical dish with a flat bottom which its material is metal or glass.
- Transfer dish or Tray: It helps in keeping the container immersed in the water bath.
- Penetration needle: stainless steel needle which is cylindrical and high polished
- Stopwatch: an automatic timer with an accuracy of 1/10 seconds.
- Thermometer: it shows the temperature in the range of 0-44 °C.
- Penetrometer: the device contains a needle. It is used to release and lock the needle in any position and allows measuring the penetration by applying a load of 100 grams with the least friction. It is important to calibrate accurately.
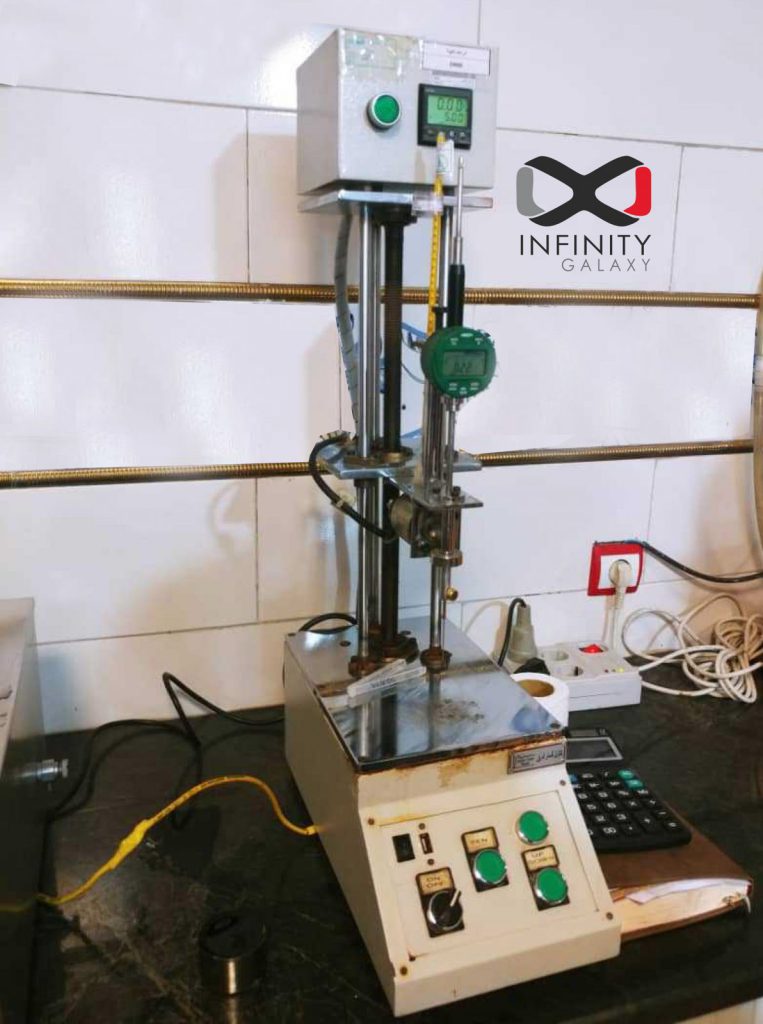

2- Procedure of Bitumen Penetration Test
- Bitumen preparing
Heat the specimen up to 90 °C and stir the melted sample until achieving consistency and the sample doesn’t have air bubble or water. Pour it into a container and let the sample cool at atmosphere temperature. Place the above assembly in a water bath at a constant temperature of 25 °C.
- Testing of bitumen penetration
Fill the transfer dish with water from the water bath. Place the sample in the transfer dish and place the whole assembly under the stand of the penetration apparatus. Release the needle on the surface of the sample with a load of 100 gr for only 5 seconds. For each sample at least three determinations are taken. It is important to use a clean needle for each determination. When measuring, the needle tip must be 10mm away from the container side. Moreover, the location of the needle in each repeat must be 10 mm apart.
It is essential that the penetration test method be performed accurately because even a small deviation can make a big difference in the results. The most common errors are as follows:
- Poor sampling and poor sample preparation
- Poor maintenance of laboratory equipment and needles
- Incorrect temperature and time
In repeated measurements for each sample, the maximum difference between the highest and lowest readings shall be:
| Acceptable Erorr Bar of Penetration Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (d-mm) | 0-49 | 50-149 | 150-249 | 250-500 |
| Maximum difference | 2 | 4 | 12 | 20 |
Penetration Test of Bitumen Conclusion
Based on the bitumen penetration test, the bitumen can be classified into different grades. In this test, the needle of the penetration test apparatus sinks to the bitumen sample for 5 seconds and measures the penetration degree based on the mm.